problem
stringlengths 18
2.25k
| gt
stringlengths 1
173
|
|---|---|
15. Given $x, y \in\left[-\frac{\pi}{4}, \frac{\pi}{4}\right], a \in \mathbf{R}$, and $x^{3}+\sin x-2 a=0,4 y^{3}+\frac{1}{2} \sin 2 y+a=0$. Then the value of $\cos (x+2 y)$ is $\qquad$ .
|
1
|
126 If $\varphi \in\left(0, \frac{\pi}{2}\right)$, among the following conclusions, the correct one is
A. $\sin (\sin \varphi)\cos \varphi>\cos (\cos \varphi)$
C. $\sin (\cos \varphi)>\cos \varphi>\cos (\sin \varphi)$
D. $\sin (\cos \varphi)<\cos \varphi<\cos (\sin \varphi)$
|
D
|
Example 7 Calculate $\frac{1}{2 \sqrt{1}+\sqrt{2}}+\frac{1}{3 \sqrt{2}+2 \sqrt{3}}$
$$
+\frac{1}{4 \sqrt{3}+3 \sqrt{4}}+\cdots+\frac{1}{100 \sqrt{99}+99 \sqrt{100}} .
$$
|
\frac{9}{10}
|
18. If the sum of the interior angles of a convex polygon is 5 times the sum of the exterior angles, then this polygon has $\qquad$ sides.
|
12
|
## Task 11/73
A train passes a kilometer post with a two-digit kilometer number. After the time $\Delta t_{1}$, it passes another kilometer post with the same digits but in reversed order.
Finally, after the additional time $\Delta t_{2}=\Delta t_{2}$, it encounters a third kilometer post, whose number is the same as the first number with a zero inserted in between.
The average speeds $v_{1}$ and $v_{2}$ during the times $\Delta t_{1}$ and $\Delta t_{2}$, respectively, are the same: $v_{1}=v_{2}$.
What are the numbers on the kilometer posts?
|
16,61,106
|
(9) Let the function $f(x)=\frac{1}{2}+\log _{2} \frac{x}{1-x}, S_{n}=\sum_{i=1}^{n-1} f\left(\frac{i}{n}\right)$, where $n \in$ $\mathbf{N}^{*}$, and $n \geqslant 2$, then $S_{n}=$ $\qquad$ .
|
\frac{n-1}{2}
|
For each $n\in\mathbb N$, the function $f_n$ is defined on real numbers $x\ge n$ by
$$f_n(x)=\sqrt{x-n}+\sqrt{x-n+1}+\ldots+\sqrt{x+n}-(2n+1)\sqrt x.$$(a) If $n$ is fixed, prove that $\lim_{x\to+\infty}f_n(x)=0$.
(b) Find the limit of $f_n(n)$ as $n\to+\infty$.
|
0
|
Good morning, I.v.
Vasya has 100 bank cards. Vasya knows that one of the cards has 1 ruble, another has 2 rubles, and so on, with the last card having 100 rubles, but he does not know how much money is on which card. Vasya can insert a card into an ATM and request a certain amount. The ATM dispenses the requested amount if it is available on the card, and does nothing if the money is not there, while swallowing the card in either case. The ATM does not show how much money was on the card. What is the largest amount of money Vasya can guarantee to get?
|
2550
|
2. For every natural number $n$, we write the sum $1^{n}+2^{n}+3^{n}+4^{n}$ as a number $\mathrm{v}$ in decimal notation. With how many zeros can these numbers end at most?
|
2
|
## Zadatak B-2.5.
Ako je $x=2017 \cdot 2018 \cdot 2021 \cdot 2022+4$, izračunajte $\sqrt{x}-2020^{2}$.
|
-2024
|
33. How many people got lost in the mountains?
Alice and the Griffin had to wait several minutes before the Tortoise Quasi gathered his strength and could continue.
- You see,一began the Tortoise Quasi.
- I don't see anything!- the Griffin cut in.
The Tortoise Quasi did not respond, only grabbing his head with his front paws again. After remaining silent for some time, he spoke again:
- Let's say... Nine people got lost in the mountains. They only had enough food for five days. Can you imagine, just five days!
Having reached this point in his story, the Tortoise Quasi was so moved by the tragedy that he could not continue from the overflow of emotions.
- Well, that's enough, there, there! - the Griffin tried to comfort him, patting his back.
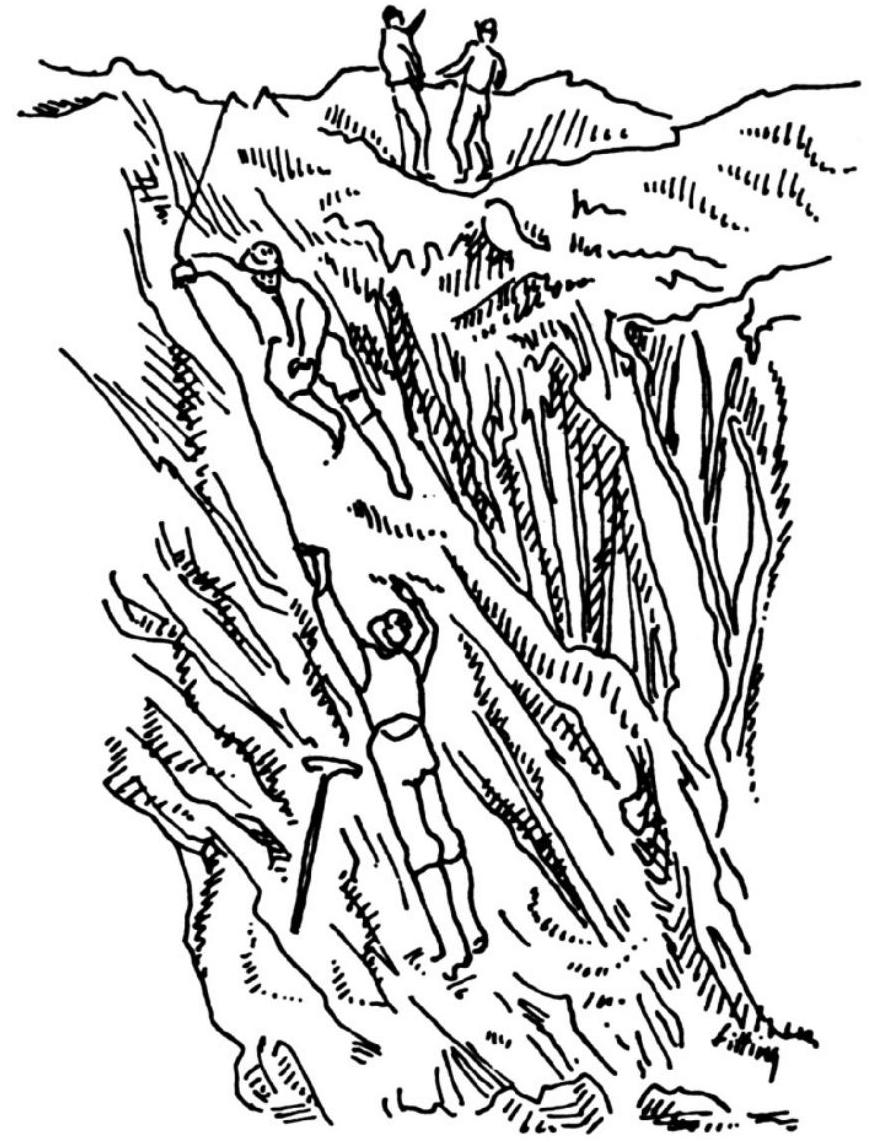
- Can you imagine what will happen to them if they are not found! - the Tortoise Quasi sobbed. - But it happened (and this is the most beautiful part of the story!)... Yes, the most beautiful part of the story is that the next day the poor souls met another group of lost people in the mountains...
- What's so beautiful about that? - the Griffin asked.
- The most beautiful part is that the first group generously shared their supplies with the second - they divided the provisions equally among everyone, after which the food lasted for another three days.
How many people were in the second group?
|
3
|
Find all $4$-tuples $(a,b,c,d)$ of natural numbers with $a \le b \le c$ and $a!+b!+c!=3^d$
|
(1, 1, 1, 1), (1, 2, 3, 2), (1, 2, 4, 3)
|
$d(n)$ shows the number of positive integer divisors of positive integer $n$. For which positive integers $n$ one cannot find a positive integer $k$ such that $\underbrace{d(\dots d(d}_{k\ \text{times}} (n) \dots )$ is a perfect square.
|
n
|
The sum of two natural numbers and their greatest common divisor is equal to their least common multiple. Determine the ratio of the two numbers.
Translating the text as requested, while maintaining the original formatting and line breaks.
|
3:2
|
## 15. The Great Mass
The main stained glass window of a modern cathedral is a circle with a diameter of 2 m, intersected by a cross formed by two perpendicular lines that intersect at a point 50 cm away from the center of the window. During the great mass, one slightly absent-minded Parisian decided to calculate the sum of the squares of the lengths of the two segments of this cross.
"Look at this! - he exclaimed. - The number of square meters is equal to the number of mortal sins ${ }^{2}$".
Why did this happen?
|
7\mathrm{~}^{2}
|
58. Compute the integral
$$
\int_{-1}^{1} \frac{d x}{1+x^{3}+\sqrt{1+x^{6}}}
$$
|
1
|
4. Wu Yu wrote three letters and three envelopes, and he needs to put each letter into the corresponding envelope, with only one letter per envelope. The number of all possible scenarios where at least one of the three letters is placed incorrectly is $\qquad$ kinds.
|
5
|
One of the roots of the equation $x^{2}+a x+b=0$ is $1+\sqrt{3}$. Find $a$ and $b$, given that they are rational.
#
|
=b=-2
|
2. Let $a$ and $b$ be integers, and the equation
$$
a x^{2}+b x+1=0
$$
has two distinct positive roots both less than 1. Then the minimum value of $a$ is
|
5
|
Example 2. Let's calculate the sum
$$
a^{2000}+\frac{1}{a^{2000}}
$$
if $a^{2}-a+1=0$.
|
-1
|
4. Let the circle $O: x^{2}+y^{2}=5$ intersect the parabola $C: y^{2}=2 p x(p>0)$ at point $A\left(x_{0}, 2\right)$, and let $AB$ be the diameter of circle $O$. A line passing through $B$ intersects $C$ at two distinct points $D, E$. Then the product of the slopes of lines $AD$ and $AE$ is $\qquad$.
|
2
|
A castle has infinitely many rooms labeled $1,2,3, \ldots$, which are divided into several halls. Suppose room $n$ is on the same hall as rooms $3 n+1$ and $n+10$ for every $n$. Determine the maximum possible number of different halls in the castle.
|
3
|
8. Given that a series of non-overlapping disks with radius $R$ can cover all lattice points (in the Cartesian coordinate system, points with both integer horizontal and vertical coordinates are lattice points) on the plane. Then $R_{\max }$ $\qquad$ 4 (fill in “greater than”, “less than”, or “equal to”).
|
less than
|
1. Given positive integers $a, b, c (a < b < c)$ form a geometric sequence, and
$$
\log _{2016} a+\log _{2016} b+\log _{2016} c=3 .
$$
Then the maximum value of $a+b+c$ is $\qquad$
|
4066273
|
9. To what power must the root $x_{0}$ of the equation $x^{11} + x^{7} + x^{3} = 1$ be raised to obtain the number $x_{0}^{4} + x_{0}^{3} - 1 ?$
|
15
|
11. (20 points) Let the sequence $\left\{A_{n}\right\}$ satisfy
$$
A_{1}=1, A_{2}=3, A_{n}=4 A_{n-1}-A_{n-2} \text {. }
$$
Find the value of $\sum_{n=1}^{+\infty} \operatorname{arccot} 2 A_{n}^{2}$.
|
\frac{\pi}{6}
|
12. Given that $x, y$ are real numbers, and $x+y=1$, find the maximum value of $\left(x^{3}+1\right)\left(y^{3}+1\right)$.
|
4
|
2. In the ellipse $\Gamma$, $A$ is one endpoint of the major axis, $B$ is one endpoint of the minor axis, and $F_{1}, F_{2}$ are the two foci. If $\overrightarrow{A F_{1}} \cdot \overrightarrow{A F_{2}}+\overrightarrow{B F_{1}} \cdot \overrightarrow{B F_{2}}=0$, then the value of $\frac{|A B|}{\left|F_{1} F_{2}\right|}$ is $\qquad$.
|
\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}
|
4. Solve the system of equations
$$
\left\{\begin{array}{l}
x^{2}+y^{2}=1 \\
x^{3}+y^{5}=1
\end{array}\right.
$$
|
(0;1),(1;0)
|
18. (1989 American High School Mathematics Examination) A real number $x$ is chosen at random between 100 and 200. If $[\sqrt{x}]=12$, then the probability that $[\sqrt{100 x}]=120$ is ( ).
A. $\frac{2}{25}$
B. $\frac{241}{2500}$
C. $\frac{1}{10}$
D. $\frac{96}{625}$
E. 1
|
\frac{241}{2500}
|
9. Solve the equation $a^{2}+2=b$ !, given that a, b belong to N. In the answer, indicate the sum of the product of all possible a and the product of all possible b (if the equation has no solutions, indicate 0; if there are infinitely many solutions, indicate 1000).
|
5
|
12. $k$ is a real number, let $f(x)=\frac{x^{4}+k x^{2}+1}{x^{4}+x^{2}+1}$. If for any three real numbers $a, b, c$ (which can be the same), there exists a triangle with side lengths $f(a), f(b), f(c)$, then the range of $k$ is $\qquad$.
|
-\frac{1}{2}<k<4
|
15.26. Into how many parts do the planes of the faces divide the space a) of a cube; b) of a tetrahedron?
|
15
|
Example 4. Find the general solution of the equation $y^{\prime \prime}+3 y^{\prime}=0$.
|
C_{1}+C_{2}e^{-3x}
|
2. Let $f(x)$ be an odd function defined on $(-\infty, 0) \cup(0,+\infty)$. When $x>0$, $x f^{\prime}(x)<0$ and $f(1)=0$. Then the solution set of the inequality $x f(x)<0$ is $\qquad$.
|
(-\infty,-1)\cup(1,+\infty)
|
## Problem Statement
Calculate the definite integral:
$$
\int_{3}^{5} \sqrt{\frac{2-x}{x-6}} d x
$$
|
\frac{2\pi}{3}
|
10. (6 points) A few hundred years ago, Columbus discovered the New World in America, and the four digits of that year are all different, their sum equals 16. If the tens digit is increased by 1, then the tens digit is exactly 5 times the units digit, so Columbus discovered the New World in America in the year $\qquad$.
将上面的文本翻译成英文,请保留源文本的换行和格式,直接输出翻译结果。
|
1492
|
B1. Accurately, without using a pocket calculator, calculate the value of the expression
$$
\frac{\cos 20^{\circ}-\sin 650^{\circ}}{\sin \frac{\pi}{12} \cdot \cos \left(-520^{\circ}\right)}+2^{2} \cdot \cos \frac{\pi}{4}
$$
Rationalize the denominator.
|
-2\sqrt{6}
|
The domain of the function $f(x) = \text{arcsin}(\log_{m}(nx))$ is a closed interval of length $\frac{1}{2013}$, where $m$ and $n$ are positive integers and $m > 1$. Find the remainder when the smallest possible sum $m+n$ is divided by $1000$.
|
371
|
Example 6 Given the sequence $\left\{a_{n}\right\}$ satisfies $a_{1}=a_{2}=1$, and $a_{n+2}=3 a_{n+1}+18 a_{n}+2^{n}\left(n \in \mathbf{N}_{+}\right)$.
Find $a_{n}$.
|
a_{n}=\frac{6^{n}}{12}-\frac{(-3)^{n}}{5}-\frac{2^{n}}{20}
|
2. Given a triangle $ABC$ and points $M, N, P$ on sides $AB, BC, CA$ respectively, such that $\overline{AM}: \overline{AB} = \overline{BN}: \overline{BC} = \overline{CP}: \overline{CA} = k$. Determine the value of $k$ for which the area of triangle $MNP$ is the smallest.
|
\frac{1}{2}
|
Task 2. (10 points) A circle touches the extensions of two sides $A B$ and $A D$ of square $A B C D$ with side $2-\sqrt{5-\sqrt{5}}$ cm. Two tangents are drawn from point $C$ to this circle. Find the radius of the circle if the angle between the tangents is $72^{\circ}$, and it is known that $\sin 36^{\circ}=\frac{\sqrt{5-\sqrt{5}}}{2 \sqrt{2}}$.
#
|
\sqrt{5-\sqrt{5}}
|
## Task B-2.4.
Pinocchio tells the truth on Mondays and Tuesdays, always lies on Saturdays, and on the other days of the week, he either tells the truth or lies. In response to the question "What is your favorite subject at school?" over six consecutive days of the week, he gave the following answers in order: "History", "Mathematics", "Geography", "Physics", "Chemistry", "Physics". What subject does Pinocchio like the most? Explain your answer.
|
History
|
3. Given a rectangular cuboid $A B C D-A_{1} B_{1} C_{1} D_{1}$, where $A D=1, A B=2, A A_{1}=3$, point $P$ is a point within the plane $A_{1} B D$. Then the minimum length of $A P$ is
|
\frac{6}{7}
|
46th Putnam 1985 Problem A5 Let f n (x) = cos x cos 2x ... cos nx. For which n in the range 1, 2, ... , 10 is the integral from 0 to 2π of f n (x) non-zero? Solution
|
3,4,7,8
|
8.46 In the Cartesian coordinate system, there is a circular arc with a central angle of $30^{\circ}$, and its center is on the $y$-axis. The number of intersection points between this arc and the curve $y=\sin x$ is
(A) 0 or 1.
(B) 0 or 1 or 2.
(C) Any natural number.
(D) 0 or any natural number.
(2nd "Hope Cup" National Mathematics Invitational Competition, 1991)
|
D
|
12. Given the quadratic function
$$
y=a(a+1) x^{2}-(2 a+1) x+1,
$$
where $a$ is a positive integer.
(1) If the graph of the function $y$ intersects the $x$-axis at points $A$ and $B$, find the length of segment $AB$;
(2) If $a$ takes the values $1, 2, \cdots, 2005$ successively, the 2005 line segments intercepted by the graph of the function $y$ on the $x$-axis are $A_{1} B_{1}, A_{2} B_{2}, \cdots, A_{2000} B_{2000}$, find the sum of the lengths of these 2005 line segments.
|
\frac{2005}{2006}
|
Let $ABCD$ be an [isosceles trapezoid](https://artofproblemsolving.com/wiki/index.php/Isosceles_trapezoid), whose dimensions are $AB = 6, BC=5=DA,$and $CD=4.$ Draw [circles](https://artofproblemsolving.com/wiki/index.php/Circle) of [radius](https://artofproblemsolving.com/wiki/index.php/Radius) 3 centered at $A$ and $B,$ and circles of radius 2 centered at $C$ and $D.$ A circle contained within the trapezoid is [tangent](https://artofproblemsolving.com/wiki/index.php/Tangent) to all four of these circles. Its radius is $\frac{-k+m\sqrt{n}}p,$ where $k, m, n,$ and $p$ are [positive integers](https://artofproblemsolving.com/wiki/index.php/Positive_integer), $n$ is not [ divisible](https://artofproblemsolving.com/wiki/index.php/Divisibility) by the [ square](https://artofproblemsolving.com/wiki/index.php/Perfect_square) of any [ prime](https://artofproblemsolving.com/wiki/index.php/Prime_number), and $k$ and $p$ are [relatively prime](https://artofproblemsolving.com/wiki/index.php/Relatively_prime). Find $k+m+n+p.$
|
134
|
Example 2. Find the length of the minor arc of the circle $\mathrm{O}: \mathrm{x}^{2}+\mathrm{y}^{2}=9$ intercepted by $\odot \mathrm{O}_{1}$ : $(x-3)^{2}+y^{2}=27$.
|
2\pi
|
8. If the inequality $\log _{\frac{1}{a}}\left(\sqrt{x^{2}+a x+5}+1\right) \cdot \log _{5}\left(x^{2}+a x+6\right)+$ $\log _{3} a \geqslant 0$ has exactly one solution for $x$, then the range of values for $a$ is $\qquad$
|
2
|
13.346. The volume of substance A is half the sum of the volumes of substances B and C, and the volume of substance B is 1/5 of the sum of the volumes of substances A and C. Find the ratio of the volume of substance C to the sum of the volumes of substances A and B.
|
1
|
Five points lie on the same line. When we list the ten distances between any two of these points, from smallest to largest, we get $2,4,5,7,8, k, 13,15,17,19$. What is the value of $k$?
|
12
|
306. Lightning Rod. A strong gust of wind broke the lightning rod's pole, causing its top to hit the ground 20 m from the base of the pole. The pole was repaired, but it broke again under a gust of wind, 5 m lower than before, and its top hit the ground 30 m from the base.
What is the height of the pole? In both cases, the broken part of the pole did not completely separate from the rest of it.
|
50\mathrm{}
|
A6. Let $x<-2$. Simplify the fraction $\frac{x^{2}-1+|x+1|}{x^{2}-2 x}$. The result is
(A) $-\frac{x+1}{x-2}$
(B) $\frac{x+1}{x}$
(C) $-\frac{x+1}{x}$
(D) 1
(E) -1
## II. PART
|
\frac{x+1}{x}
|
8. Given the equation of circle $C$ as $x^{2}+y^{2}-8 x+15=0$, if there exists at least one point on the line $y=k x-2(k \in \mathbf{R})$ such that a circle with this point as its center and 1 as its radius has a common point with circle $C$, then the maximum value of $k$ is $\qquad$.
|
\frac{4}{3}
|
A3. Determine the number of pairs of integers $(m, n)$ such that
$$
\sqrt{n+\sqrt{2016}}+\sqrt{m-\sqrt{2016}} \in \mathbb{Q}
$$
|
1
|
1. The mean age of the members of a jazz band is 21 . The saxophonist, singer and trumpeter are 19,20 and 21 years old respectively. The other three musicians are all the same age. How old are they?
A 21
B 22
C 23
D 24
E 26
|
22
|
6. Let $S=\left\{\left(s_{1}, s_{2}, \cdots, s_{6}\right) \mid s_{i} \in\{0,1\}\right\}$, for any $x, y \in S, x=\left(x_{1}, x_{2}, \cdots, x_{6}\right), y=$ $\left(y_{1}, y_{2}, \cdots, y_{6}\right)$ define:
(1) $x=y \Leftrightarrow \sum_{i=1}^{6}\left(x_{i}-y_{i}\right)^{2}=0$;
(2) $x y=x_{1} y_{1}+x_{2} y_{2}+\cdots+x_{6} y_{6}$.
If a non-empty set $T \subseteq S$, and for any $u, v \in T, u \neq v$, we have $u v \neq 0$, then the maximum number of elements in the set $T$ is ( ).
(A) 62
(B) 52
(C) 42
(D) 32
|
32
|
Find the value of $ a$ for which $ \int_0^{\pi} \{ax(\pi ^ 2 \minus{} x^2) \minus{} \sin x\}^2dx$ is minimized.
|
\frac{315}{4 \pi^6}
|
3. For the equation in $x$, $\left|\frac{x^{2}}{x-1}\right|=a$, there are only two distinct real roots. Then the range of the constant $a$ is ( ).
(A) $a>0$
(B) $a \geqslant 4$
(C) $2<a<4$
(D) $0<a<4$
|
D
|
6. (51st Czech and Slovak Mathematical Olympiad (Final) Problem) Let $\mathrm{R}^{+}$ denote the set of positive real numbers. Find the function $f: \mathrm{R}^{+} \rightarrow \mathrm{R}^{+}$, such that for all $x, y \in \mathbf{R}$, we have $f(x f(y))=f(x y)+x$.
|
f(x)=x+1
|
2. $\sin ^{2} 100^{\circ}-\sin 50^{\circ} \sin 70^{\circ}=$
|
\frac{1}{4}
|
8. In an acute-angled triangle $ABC$ with sides $AB=4, AC=3$, a point $N$ is marked on the median $AM$ such that $\angle BNM = \angle MAC$. Find the length of the segment $BN$.
|
3
|
## Problem Statement
Calculate the limit of the function:
$\lim _{x \rightarrow \pi}\left(\operatorname{ctg}\left(\frac{x}{4}\right)\right)^{1 / \cos \left(\frac{x}{2}\right)}$
|
e
|
4. As shown in Figure $2, \odot O$ is internally tangent to $\odot O^{\prime}$ at point $P, \odot O$'s chord $A B$ is tangent to $\odot O^{\prime}$ at point $C$, and $A B / / O O^{\prime}$. If the area of the shaded part is $4 \pi$, then the length of $A B$ is $\qquad$
|
4
|
Example 6. When $|x+1| \leqslant 6$, the maximum value of the function $y=x|x|$ $-2 x+1$ is $\qquad$. (1994, National Junior High School Competition)
|
16
|
# Problem 8.3
## Condition:
Given triangle $\mathrm{ABC}$, where $2 \mathrm{BC}=\mathrm{AC}$ and angle $\mathrm{C}=46^{\circ}$. On the ray $\mathrm{BC}$, segment $\mathrm{CM}=$ CB is marked. Then, from point M, a perpendicular is drawn to the line containing the median of triangle $\mathrm{ABC}$, drawn from vertex $\mathrm{B}$, and the intersection point is N. What is the measure of angle CMN? Express your answer in degrees.
|
23
|
5-6. A rectangular table of size $x$ cm $\times 80$ cm is covered with identical sheets of paper of size 5 cm $\times 8$ cm. The first sheet touches the bottom left corner, and each subsequent sheet is placed one centimeter higher and one centimeter to the right of the previous one. The last sheet touches the top right corner. What is the length $x$ in centimeters?
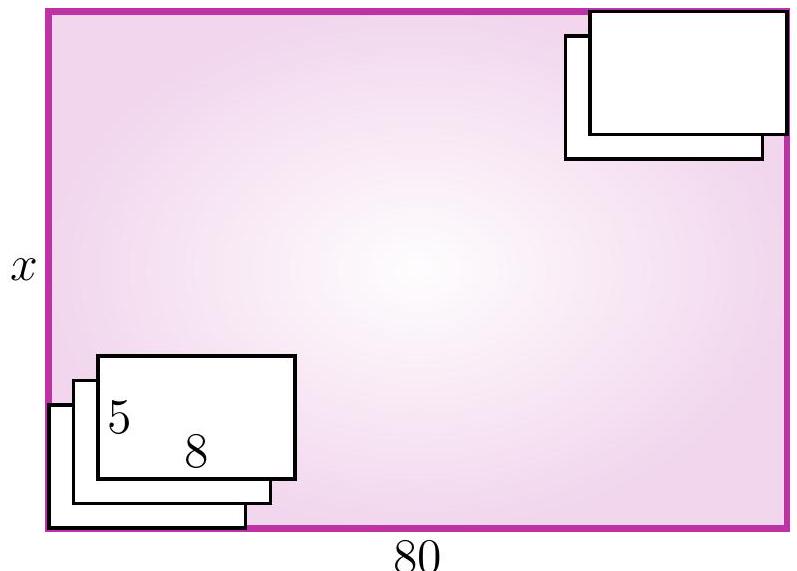
|
77
|
10. Two different parabolas $y=x^{2}+k x+1$ and $y=x^{2}-x-k$ pass through the same point on the $x$-axis when the value of the real number $k$ is $\qquad$.
|
2
|
4.035. When the thirteenth term of an arithmetic progression is divided by the third term, the quotient is 3, and when the eighteenth term is divided by the seventh term, the quotient is 2 and the remainder is 8. Determine the common difference and the first term of the progression.
|
4,12
|
1. The range of the inclination angle of the line $x \cdot \cos \alpha+y+1=0$ is
|
[0,\frac{\pi}{4}]\cup[\frac{3\pi}{4},\pi)
|
Let $a<b<c<d<e$ be real numbers. We calculate all possible sums of two distinct numbers among these five numbers. The three smallest sums are 32, 36, and 37, and the two largest sums are 48 and 51. Find all possible values of $e$.
## High School Statements
|
\frac{55}{2}
|
Example 6 There are 1994 matches on the table, two children, A and B, take turns to take 1, 2 or 3 matches each time, the one who can take the last match wins. Now A takes first, which child will win? How should he play to win this game?
|
A
|
| Two tangents drawn from one point | |
| :---: | :---: | :---: |
| | Properties and characteristics of tangents | Slo |
| | Auxiliary similar triangles Pythagoras' theorem (direct and inverse) | |
Two tangents are drawn from one point to a circle. The length of the tangent is 156, and the distance between the points of tangency is 120. Find the radius of the circle.
|
65
|
22) A particle of mass m moving at speed $v_0$ collides with a particle of mass $M$ which is originally at rest. The fractional momentum transfer $f$ is the absolute value of the final momentum of $M$ divided by the initial momentum of $m$.
The fractional energy transfer is the absolute value of the final kinetic energy of $M$ divided by the initial kinetic energy of $m$.
If the collision is perfectly elastic, under what condition will the fractional energy transfer between the two objects be a maximum?
A) $\frac{m}{M} \ll 1$
B) $0.5 < \frac{m}{M} < 1$
C) $m = M$
D) $1 < \frac{m}{M} < 2$
E) $\frac{m}{M} \gg 1$
|
m = M
|
For each positive integer $n$, let $s(n)$ be the sum of the digits of $n$. Find the smallest positive integer $k$ such that
\[s(k) = s(2k) = s(3k) = \cdots = s(2013k) = s(2014k).\]
|
9999
|
1. Martians love to dance dances where they have to hold hands. In the dance "Pyramid," no more than 7 Martians can participate, each of whom has no more than three hands. What is the maximum number of hands that the dancers can have if any hand of one Martian holds exactly one hand of another Martian?
|
20
|
$14.4 .23^{\star \star}$ Find all prime numbers $p$ such that the sum of all divisors of $p^{4}$ is a perfect square.
|
3
|
Example 7 Solve the equation
$$
\sqrt{x^{2}+\sqrt{3} x+\frac{7}{4}}+\sqrt{x^{2}-3 \sqrt{3} x+\frac{31}{4}}=4 \text {. }
$$
|
x=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}
|
13.117. A cyclist traveled 60 km from point $A$ to point $B$. On the return trip, he rode the first hour at the same speed, then stopped for 20 minutes. Resuming his journey, he increased his speed by 4 km/h and therefore spent as much time traveling from $B$ to $A$ as he did traveling from $A$ to $B$. Determine the cyclist's speed on the trip from $A$ to $B$.
|
20
|
18. Let $x_{1}, x_{2}, \cdots, x_{n}$ and $a_{1}, a_{2}, \cdots, a_{n}$ be two sets of arbitrary real numbers $(n \geqslant 2)$ satisfying the conditions: $1^{\circ} . \sum_{i=1}^{n} x_{i}=0$; $2^{\circ} . \sum_{i=1}^{n}\left|x_{i}\right|=1 ; 3^{\circ} . a_{1} \geqslant a_{2} \geqslant \cdots \geqslant a_{n}$. Try to find the minimum value of $A$ such that the inequality $\left|\sum_{i=1}^{n} a_{i} x_{i}\right| \leqslant A\left(a_{1}-a_{n}\right)$ holds.
|
\frac{1}{2}
|
3. Let the first term and common difference of an arithmetic sequence be non-negative integers, the number of terms be no less than 3, and the sum of all terms be $97^{2}$, then the number of such sequences is ( ).
A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. 5
|
4
|
97. A class of students goes to plant trees under the leadership of their homeroom teacher, and the students are exactly divided into three groups. If the teacher and students each plant the same number of trees, and they plant a total of 1073 trees, then on average each person plants $\qquad$ trees.
|
29
|
6. Given the sequence $\left\{a_{n}\right\}$
satisfies
$$
a_{n}=\sqrt{1+\frac{1}{n^{2}}+\frac{1}{(n+1)^{2}}}(n \geqslant 1),
$$
and its first $n$ terms sum is $S_{n}$. Then $\left[S_{n}\right]=$ $\qquad$ ( [ $x$ denotes the greatest integer not exceeding the real number $x$ ).
|
n
|
There are $281 n(n>3)$ football teams that have played $k$ matches, with each pair of teams playing at most one match, and there are no ties. It turns out that exactly one team remains undefeated. Additionally, it is found that for any two teams $A$ and $B$, there exists another team $C$ such that either $A$ beats $C$ and $B$ beats $C$; or $C$ beats $A$ and $C$ beats $B$. Find the minimum value of $k$, denoted as $f(n)$.
|
2n-2
|
8. For a finite set
$$
A=\left\{a_{i} \mid 1 \leqslant i \leqslant n, i \in \mathbf{Z}_{+}\right\}\left(n \in \mathbf{Z}_{+}\right) \text {, }
$$
let $S=\sum_{i=1}^{n} a_{i}$, then $S$ is called the "sum" of set $A$, denoted as $|A|$. Given the set $P=\{2 n-1 \mid n=1,2, \cdots, 10\}$, all subsets of $P$ containing three elements are $P_{1}, P_{2}, \cdots, P_{k}$. Then $\sum_{i=1}^{k}\left|P_{i}\right|=$ $\qquad$ .
|
3600
|
Let $a$ be the sum of the numbers:
$99 \times 0.9$
$999 \times 0.9$
$9999 \times 0.9$
$\vdots$
$999\cdots 9 \times 0.9$
where the final number in the list is $0.9$ times a number written as a string of $101$ digits all equal to $9$.
Find the sum of the digits in the number $a$.
|
891
|
14. The roots of the equation $x^{2}-2 x-a^{2}-a=0$ are $\left(\alpha_{a}\right.$,
$$
\begin{array}{r}
\left.\beta_{a}\right)(a=1,2, \cdots, 2011) . \\
\text { Find } \sum_{a=1}^{2011}\left(\frac{1}{\alpha_{a}}+\frac{1}{\beta_{a}}\right) \text { . }
\end{array}
$$
|
-\frac{2011}{1006}
|
16. The digits from 1 to 9 are randomly arranged to make a 9 -digit number. What is the probability that the resulting number is divisible by 18 ?
A $\frac{1}{3}$
B $\frac{4}{9}$
C $\frac{1}{2}$
D $\frac{5}{9}$
$\mathrm{E} \frac{3}{4}$
|
\frac{4}{9}
|
A set of positive integers is said to be [i]pilak[/i] if it can be partitioned into 2 disjoint subsets $F$ and $T$, each with at least $2$ elements, such that the elements of $F$ are consecutive Fibonacci numbers, and the elements of $T$ are consecutive triangular numbers. Find all positive integers $n$ such that the set containing all the positive divisors of $n$ except $n$ itself is pilak.
|
30
|
14. In 1993, American mathematician F. Smarandache proposed many number theory problems, attracting the attention of scholars both at home and abroad. One of these is the famous Smarandache function. The Smarandache function of a positive integer \( n \) is defined as
\[
S(n)=\min \left\{m \left| m \in \mathbf{Z}_{+}, n \right| m!\right\},
\]
For example, \( S(2)=2, S(3)=3, S(6)=3 \).
(1) Find the values of \( S(16) \) and \( S(2016) \);
(2) If \( S(n)=7 \), find the maximum value of the positive integer \( n \);
(3) Prove that there are infinitely many composite numbers \( n \) such that \( S(n)=p \), where \( p \) is the largest prime factor of \( n \).
|
5040
|
Given a positive integer $n>1$. Denote $T$ a set that contains all ordered sets $(x;y;z)$ such that $x,y,z$ are all distinct positive integers and $1\leq x,y,z\leq 2n$. Also, a set $A$ containing ordered sets $(u;v)$ is called [i]"connected"[/i] with $T$ if for every $(x;y;z)\in T$ then $\{(x;y),(x;z),(y;z)\} \cap A \neq \varnothing$.
a) Find the number of elements of set $T$.
b) Prove that there exists a set "connected" with $T$ that has exactly $2n(n-1)$ elements.
c) Prove that every set "connected" with $T$ has at least $2n(n-1)$ elements.
|
2n(2n-1)(2n-2)
|
Three, (25 points) Given that $a$ and $b$ are integers, and satisfy $a-b$ is a prime number, $ab$ is a perfect square. If $a \geqslant 2011$, find the minimum value of $a$.
|
2025
|
B4. A circle with radius $r=4$ has its center at one of the vertices of the ellipse $b^{2} x^{2}+a^{2} y^{2}=a^{2} b^{2}$ and passes through both foci and the other vertex. Write the equation of the ellipse $(a>b)$!
## Solutions to problems
## First year
I. PART
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- |
| $\mathrm{D}$ | $\mathrm{D}$ | $\mathrm{E}$ | $\mathrm{E}$ | $\mathrm{A}$ | $\mathrm{B}$ |
|
x^{2}+4y^{2}=16
|
Find all functions $f: \mathbb{R} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}$ that satisfy
$$
f(x y-1)+f(x) f(y)=2 x y-1
$$
for all $x, y \in \mathbb{R}$.
|
f(x)=x \text{ or } f(x)=-x^2
|
## 40. Tennis Tournament
199 people have registered to participate in a tennis tournament. In the first round, pairs of opponents are selected by lottery. The same process is used to select pairs in the second, third, and all subsequent rounds. After each match, one of the two opponents is eliminated, and whenever the number of participants in the tournament is odd, one of them skips the current round.
Assume that in each match between two tennis players, a new can of balls is used. How many cans of balls will be needed for the entire tournament?
|
198
|
Task B-1.1. Factorize the following expression into factors that cannot be further factorized
$$
x\left(x^{2}-2\right)+4-\frac{1}{2}(x+2)^{2}
$$
|
\frac{1}{2}(x-2)(x+2)(2x-1)
|
17. Person A walks from home to Person B's home. At the same time, Person B rides a bicycle from home towards Person A's home. Each maintains a constant speed, and Person B's cycling speed is 5 times Person A's walking speed. It is known that the distance between the two homes is 10560 feet, and Person A's stride length is 2.5 feet. When Person A meets Person B, Person A has walked ( ) steps.
(A) 704
(B) 845
(C) 1056
(D) 1760
(E) 3520
|
704
|
4. Passing through point $A(1,-4)$, and parallel to the line $2 x+3 y+5=0$ the equation of the line is
|
2x+3y+10=0
|
4. Given $x \cdot y \in\left[-\frac{\pi}{4} \cdot \frac{\pi}{4}\right], a \in \mathbf{R}$, and $\left\{\begin{array}{l}x^{3}+\sin x-2 a=0 \\ 4 y^{3}+\frac{1}{2} \sin 2 y-a=0\end{array}\right.$, then $\cos (x+2 y)=$
Translate the above text into English, please retain the original text's line breaks and format, and output the translation result directly.
|
1
|
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.