problem
stringlengths 18
2.25k
| gt
stringlengths 1
173
|
|---|---|
145. Find $\lim _{x \rightarrow 0} \frac{1-\cos 8 x}{2 x^{2}}$.
|
16
|
## Task 23/89
A sequence is given by the formation rule
$$
a_{k}=p \cdot k \cdot(k+1)+1
$$
where $p$ is a prime number and $k>0$. The 7th term is the square of a prime number $P$. Determine all possible pairs $(p ; P)$.
---
|
(3;13)
|
Problem 4. All students in the class scored different numbers of points (positive integers) on the test, with no duplicate scores. In total, they scored 119 points. The sum of the three lowest scores is 23 points, and the sum of the three highest scores is 49 points. How many students took the test? How many points did the winner score?
|
10
|
## Task A-2.8. (10 points)
Determine all integers $x$ for which $x^{2}+3 x+24$ is a square of some integer.
|
-23,-8,5,20
|
13.019. Two snow-clearing machines are working on snow removal. The first can clear the entire street in 1 hour, while the second can do it in $75\%$ of this time. Starting the cleaning simultaneously, both machines worked together for 20 minutes, after which the first machine stopped. How much more time is needed for the second machine to finish the work?
|
10
|
2. In the buses of a travel agency, members of a tourist group need to be arranged so that each bus has the same number of tourists. At the beginning, 22 tourists entered each bus, leaving one tourist unscheduled. However, one bus left empty, and the tourists were then evenly distributed among the remaining buses. How many tourists and buses were there at the beginning, if no more than 32 tourists entered each bus?
|
529
|
8. Let non-negative real numbers $a, b, c$ satisfy $ab + bc + ca = a + b + c > 0$. Then the minimum value of $\sqrt{ab} + \sqrt{bc} + \sqrt{ca}$ is ( ).
(A) 2
(B) 3
(C) $\sqrt{3}$
(D) $2 \sqrt{2}$
|
2
|
11.2. In a box, there are white and blue balls, with the number of white balls being 8 times the number of blue balls. It is known that if you pull out 100 balls, there will definitely be at least one blue ball among them. How many balls are there in the box?
|
108
|
## Task 3 - 260733
Let $ABC$ be an acute-angled triangle; its circumcircle $k$ has the center $M$. The ray from $A$ through $M$ intersects $k$ at $D$, the ray from $B$ through $M$ intersects $k$ at $E$, the ray from $C$ through $M$ intersects $k$ at $F$.
Determine the ratio of the areas of the hexagon $A F B D C E$ and the triangle $A B C$!
|
2:1
|
Example 2 Let $X_{n}=\{1,2, \cdots, n\}$. Find $\sum_{A \subseteq X_{n}} S(A)$, where $S(A)$ denotes the sum of all elements in $A$, and $S(\varnothing)=0$.
|
n(n+1) 2^{n-2}
|
20th USAMO 1991 Problem 1 An obtuse angled triangle has integral sides and one acute angle is twice the other. Find the smallest possible perimeter. Solution
|
77
|
In the diagram shown, each figure after Figure 1 is formed by joining two rectangles to the bottom of the previous figure. Each individual rectangle has dimensions $10 \mathrm{~cm}$ by $5 \mathrm{~cm}$. If Figure $n$ has a perimeter of $710 \mathrm{~cm}$, the value of $n$ is
(A) 29
(B) 43
(C) 66
(D) 172
(E) 65
|
66
|
6. For each integer $n \geq 1$, define $a_{n}=\left[\frac{n}{[\sqrt{n}]}\right]$, where $[x]$ denotes the largest integer not exceeding $x$, for any real number $x$. Find the number of all $n$ in the set $\{1,2,3, \ldots, 2010\}$ for which $a_{n}>a_{n+1}$.
|
43
|
6. $a, b, c$ are all positive integers, and satisfy $a b+b c=$ $3984, a c+b c=1993$. Then the maximum value of $a b c$ is $\qquad$
Translate the above text into English, please retain the original text's line breaks and format, and output the translation result directly.
|
3982
|
$25 \cdot 23$ In the Cartesian coordinate system, the equation
$$
\frac{|x+y|}{2 a}+\frac{|x-y|}{2 b}=1
$$
$(a, b$ are two different positive numbers) represents the curve
(A) Triangle.
(B) Square.
(C) Non-square rectangle.
(D) Non-square rhombus.
(China High School Mathematics League, 1994)
|
D
|
2. $x, y \in \mathbf{R}$, and satisfy $\left\{\begin{array}{l}(x+1)^{\frac{3}{5}}+2023(x+1)=-2023, \\ (y+1)^{\frac{3}{5}}+2023(y+1)=2023\end{array}\right.$, then $x+y=$
|
-2
|
8. One or two? Let's take all natural numbers from 1 to 1000000 and for each of them, calculate the sum of its digits. For all the resulting numbers, we will again find the sum of their digits. We will continue this process until all the resulting numbers are single-digit. Among the million resulting numbers, 1 and 2 will appear. Which number will be more frequent: 1 or 2?
|
1
|
1. Positive integers $x_{1}, x_{2}, \cdots, x_{n}$ satisfy $x_{1}+x_{2}+\cdots+x_{n}=$ $m$ (constant). Try to find the maximum value of $f=x_{1}^{2}+x_{2}^{2}+\cdots+x_{n}^{2}$.
|
(n-1)+(m-n+1)^2
|
Let $k \geq 1$ be an integer.
We consider $4 k$ chips, $2 k$ of which are red and $2 k$ of which are blue. A sequence of those $4 k$ chips can be transformed into another sequence by a so-called move, consisting of interchanging a number (possibly one) of consecutive red chips with an equal number of consecutive blue chips. For example, we can move from $r \underline{b b b r} \underline{r} b$ to $r \underline{r r} b r \underline{b b b}$ where $r$ denotes a red chip and $b$ denotes a blue chip.
Determine the smallest number $n$ (as a function of $k$ ) such that starting from any initial sequence of the $4 k$ chips, we need at most $n$ moves to reach the state in which the first $2 k$ chips are red.
#
|
k
|
A6 The exact value of the expression $\sqrt[6]{0.125^{-0.6}}$ is:
(A) $\sqrt[3]{2}$
(B) $\sqrt{2}$
(C) $\sqrt[3]{5}$
(D) $\sqrt[6]{2}$
(E) $\sqrt[6]{5}$
## II. PART
|
\sqrt[3]{2}
|
1. Given the inequality $a x+3 \geqslant 0$ has positive integer solutions of $1,2,3$. Then the range of values for $a$ is $\qquad$ .
|
-1 \leqslant a<-\frac{3}{4}
|
Find the largest natural number in which each non-edge digit is less than the arithmetic mean of the adjacent digits.
#
|
96433469
|
Do either $(1)$ or $(2)$:
$(1)$ Let $C_a$ be the curve $(y - a^2)^2 = x^2(a^2 - x^2).$ Find the curve which touches all $C_a$ for $a > 0.$ Sketch the solution and at least two of the $C_a.$
$(2)$ Given that $(1 - hx)^{-1}(1 - kx)^{-1} = \sum_{i\geq0}a_i x^i,$ prove that $(1 + hkx)(1 - hkx)^{-1}(1 - h^2x)^{-1}(1 - k^2x)^{-1} = \sum_{i\geq0} a_i^2 x^i.$
|
y = \frac{3x^2}{4}
|
$11 \cdot 31$ Suppose 1987 can be written as a three-digit number $\overline{x y z}$ in base $b$, and $x+y+z=$ $1+9+8+7$, try to determine all possible $x, y, z$ and $b$.
(19th Canadian Mathematics Competition, 1987)
|
5,9,11,b=19
|
1.2. Inside the rectangle $A B C D$, whose sides are $A B=C D=15$ and $B C=A D=10$, there is a point $P$ such that $A P=9, B P=12$. Find $C P$.
|
10
|
1. If $f(x)=x^{3}-3 x+m$ takes any three numbers $a, b, c$ in the interval $[0,2]$, there exists a triangle with side lengths $f(a), f(b), f(c)$, then the range of $m$ is $\qquad$
|
(6,+\infty)
|
Consider the sequence $ a_1\equal{}\frac{3}{2}, a_{n\plus{}1}\equal{}\frac{3a_n^2\plus{}4a_n\minus{}3}{4a_n^2}.$
$ (a)$ Prove that $ 1<a_n$ and $ a_{n\plus{}1}<a_n$ for all $ n$.
$ (b)$ From $ (a)$ it follows that $ \displaystyle\lim_{n\to\infty}a_n$ exists. Find this limit.
$ (c)$ Determine $ \displaystyle\lim_{n\to\infty}a_1a_2a_3...a_n$.
|
1
|
## Problem 1.
A convex polyhedron has 12 square faces, 8 regular hexagonal faces, and 6 regular octagonal faces. At each vertex of the polyhedron, exactly one square, one hexagon, and one octagon meet. How many segments connecting pairs of vertices of the polyhedron are interior to it, that is, are neither edges nor contained in a face?
|
840
|
2.1. How many terms will there be if we expand the expression $\left(4 x^{3}+x^{-3}+2\right)^{2016}$ and combine like terms?
|
4033
|
4. On each field of the chessboard, a number is written. The sum of the numbers written on any four fields that form a knight's path (in the shape of the letter Г) is constant. How many different numbers are written on the board? Explain your answer.
|
2
|
2. Given $a=\sqrt{3}-1$. Then $a^{2012}+2 a^{2011}-2 a^{2010}=$
|
0
|
## Problem Statement
Calculate the definite integral:
$$
\int_{1}^{8} \frac{5 \sqrt{x+24}}{(x+24)^{2} \cdot \sqrt{x}} d x
$$
|
\frac{1}{8}
|
88 The range of the function $y=\sqrt{x-4}+\sqrt{15-3 x}$ is
A. $[1,2]$
B. $(0,2]$
C. $(0, \sqrt{3}]$
D. $[0,+\infty)$
|
1\leqslanty\leqslant2
|
What is the maximum number of sides a convex polygon can have if its interior angles form an arithmetic sequence with a difference of $d=1^{\circ}$?
|
27
|
2. Find the equation of the circle passing through the intersection points of the two circles
$$
x^{2}+y^{2}+6 x-4=0 \text { and } x^{2}+y^{2}+6 y-28=0
$$
and whose center lies on the line $x-y-4=0$.
|
\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^{2}+\left(y+\frac{7}{2}\right)^{2}=\frac{178}{4}
|
Two rectangles $P Q U V$ and $W S T V$ overlap as shown. What is the area of $P Q R S T V$ ?
(A) 35
(B) 24
(C) 25
(D) 17
(E) 23
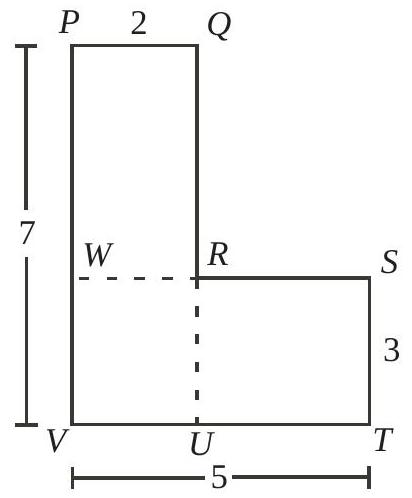
|
23
|
I5.3 In the figure, $L_{1}$ and $L_{2}$ are tangents to the three circles. If the radius of the largest circle is 18 and the radius of the smallest circle is $4 b$, find $c$, where $c$ is the radius of the circle $W$.
|
12
|
I1.2 If $\left\{\begin{array}{c}x+y=2 \\ x y-z^{2}=a \\ b=x+y+z\end{array}\right.$, find the value of $b$.
|
2
|
57. The number $123456789(10)(11)(12)(13)(14)$ is written in the base-15 numeral system, i.e., this number is equal to
(14) $+(13) \cdot 15+(12) \cdot 15^{2}+(11) \cdot 15^{3}+\ldots+2 \cdot 15^{12}+15^{13}$. What remainder does it give when divided by 7?
|
0
|
6. An increasing sequence of positive integers $\left\{a_{n}\right\}$ has the following property: for any $n \in \mathbf{N}_{+}$, it holds that $a_{n+2}=a_{n+1}+a_{n}$, and $a_{7}=120, a_{8}$ is ( ).
A. Uncertain
B. Equal to 194
C. Equal to 200
D. Equal to 216
|
194
|
17. On the blackboard, there are $n$ consecutive positive integers starting from 1. After erasing one of these numbers, the average of the remaining numbers is $36 \frac{2}{5}$. The number that was erased is $\qquad$ .
|
8
|
On a typical morning Aiden gets out of bed, goes through his morning preparation, rides the bus, and walks from the bus stop to work arriving at work 120 minutes after getting out of bed. One morning Aiden got out of bed late, so he rushed through his morning preparation getting onto the bus in half the usual time, the bus ride took 25 percent longer than usual, and he ran from the bus stop to work in half the usual time it takes him to walk arriving at work 96 minutes after he got out of bed. The next morning Aiden got out of bed extra early, leisurely went through his morning preparation taking 25 percent longer than usual to get onto the bus, his bus ride took 25 percent less time than usual, and he walked slowly from the bus stop to work taking 25 percent longer than usual. How many minutes after Aiden got out of bed did he arrive at work that day?
|
126
|
6. Given non-zero vectors $\overrightarrow{A B}$ and $\overrightarrow{A C}$ satisfy
$$
\left(\frac{\overrightarrow{A B}}{|\overrightarrow{A B}|}+\frac{\overrightarrow{A C}}{|\overrightarrow{A C}|}\right) \cdot \overrightarrow{B C}=0 \text {, }
$$
and $\frac{\overrightarrow{A B}}{|\overrightarrow{A B}|} \cdot \frac{\overrightarrow{A C}}{|\overrightarrow{A C}|}=\frac{1}{2}$.
Then $\triangle A B C$ is ( ).
(A) a triangle with all sides of different lengths
(B) a right triangle
(C) an isosceles but not equilateral triangle
(D) an equilateral triangle
|
D
|
2. In triangle $ABC$, the bisector $BD$ is drawn, and in triangles $ABD$ and $CBD$ - the bisectors $DE$ and $DF$ respectively. It turned out that $EF \parallel AC$. Find the angle $DEF$. (I. Rubanov)
|
45
|
Example 1 Let $P(x)$ be a polynomial of degree $2n$, such that
$$
\begin{array}{l}
P(0)=P(2)=\cdots=P(2 n)=0, \\
P(1)=P(3)=\cdots=P(2 n-1)=2, \\
P(2 n+1)=-6 .
\end{array}
$$
Determine $n$ and $P(x)$.
|
P(x)=-2 x^{2}+4 x
|
Task B-1.4. King Hiero of Syracuse gave 16 pounds of gold and 4 pounds of silver to have a crown made from this material. When the crown was finished, it weighed 20 pounds, but the king still asked the great mathematician Archimedes to test whether a certain amount of gold had been replaced by an equal weight of silver.
Archimedes submerged the crown in water and found that it had lost $1 \frac{1}{4}$ pounds in weight. Knowing that 20 pounds of gold lose 1 pound of their weight in water, and 21 pounds of silver lose 2 pounds of their weight in water, Archimedes determined by calculation that indeed a certain amount of gold had been replaced by silver. What is this amount of gold?
|
\frac{29}{19}
|
12. Find the 2020th term of the following sequence:
$$
1,1,3,1,3,5,1,3,5,7,1,3,5,7,9,1,3,5,7,9,11, \ldots
$$
|
7
|
## 51. Congratulations from Methuselah
Every New Year, starting from the first year of our era, Methuselah, who is still alive to this day, sends a greeting to his best friend, who, naturally, has changed many times over the centuries and decades. However, the formula for the greeting, on the contrary, has remained unchanged for almost two millennia. It is very simple: "Happy New Year 1", "Happy New Year 2", "Happy New Year 3", and so on, "Happy New Year 1978" and finally, "Happy New Year 1979".
Which digit has Methuselah used the least so far?
|
0
|
4. In a convex quadrilateral $ABCD$, it is known that $AB=2AD$, $BC=1$, $\angle ABC=\angle BCD=60^{\circ}$, $\angle ADC=$ $90^{\circ}$. Then the length of $AB$ is ( ).
(A) $\frac{3-\sqrt{3}}{4}$
(B) $\frac{3-\sqrt{3}}{2}$
(C) $2-\sqrt{3}$
(D) $2 \sqrt{3}-3$
|
B
|
Given two sequences of positive numbers $\{a_k\}$ and $\{b_k\} \ (k \in \mathbb N)$ such that:
[b](i)[/b] $a_k < b_k,$
[b](ii) [/b] $\cos a_kx + \cos b_kx \geq -\frac 1k $ for all $k \in \mathbb N$ and $x \in \mathbb R,$
prove the existence of $\lim_{k \to \infty} \frac{a_k}{b_k}$ and find this limit.
|
0
|
5. What is the sum of the coefficients of the expansion $(x+2 y-1)^{6}$ ?
|
64
|
27.23. Compare the numbers $\log _{5} 7$ and $\log _{13} 17$.
|
\log_{5}7>\log_{13}17
|
13. (5 points)
The 5 members of the Sheep Team are participating in a competitive selection match. 2 of them have only a perfect score in "climbing", another 2 have only a perfect score in "jumping", and 1 person has a perfect score in both "climbing" and "jumping". Now, 2 people need to be selected from these 5 to enter the final, with the requirement that the selected 2 people must include one with a perfect score in "climbing" and one with a perfect score in "jumping". There are $\qquad$ different ways to select them.
|
8
|
10. Let the line pass through the intersection of the lines $3 x+2 y-5=0, 2 x+3 y-5=0$, and have a y-intercept of -5, then the equation of this line is $\qquad$ .
|
6x-y-5=0
|
Example 4 (1992 "Friendship Cup" International Mathematics Competition Question) Find the largest natural number $x$, such that for every natural number $y$, $x$ divides $7^{y}+12 y-1$.
|
18
|
Task B-2.1. Draw in the complex plane the set of points $(x, y)$, associated with complex numbers $z=x+yi$, for which
$$
\operatorname{Re} z \cdot \operatorname{Im} z<0 \quad \mathrm{and} \quad|z|^{2} \leq \operatorname{Im}\left(z^{2}\right)+1
$$
Calculate the area of this set of points.
|
1
|
24th ASU 1990 Problem 6 Find three non-zero reals such that all quadratics with those numbers as coefficients have two distinct rational roots.
|
1,2,-3
|
11.2. A line with a positive slope passes through the point (0, 2020) and intersects the parabola $y=x^{2}$ at two points with integer coordinates. What values can the slope take? List all possible options and explain why there are no others.
|
81,192,399,501,1008,2019
|
4. For a finite sequence $P=\left(p_{1}, p_{2}, \cdots, p_{n}\right)$, the Cesàro sum of $P$ (Cesàro being a mathematician's name) is defined as $\frac{1}{n}\left(S_{1}+S_{2}+\cdots+S_{n}\right)$, where $S_{k}=p_{1}+p_{2}+\cdots+p_{k}(1 \leqslant k \leqslant n)$. If a 99-term sequence $\left(p_{1}, p_{2}, \cdots, p_{99}\right)$ has a Cesàro sum of 1000, then the Cesàro sum of the 100-term sequence $\left(1, p_{1}, p_{2}, \cdots, p_{99}\right)$ is ( ).
A. 990
B. 991
C. 992
D. 993
|
991
|
1. [5] Determine the remainder when $1+2+\cdots+2014$ is divided by 2012 .
|
1009
|
2. (2000 National High School Mathematics League Question) The minimum value of the distance from the lattice points (points with integer coordinates) to the line $y=$ $\frac{5}{3} x+\frac{4}{5}$ is ( )
A. $\frac{\sqrt{34}}{170}$
B. $\frac{\sqrt{34}}{85}$
C. $\frac{1}{20}$
D. $\frac{1}{30}$
|
\frac{\sqrt{34}}{85}
|
In how many ways can the integers from 1 to 2021 be colored such that each integer is colored either blue, green, or red, and such that two consecutive integers are never the same color?
|
3\cdot2^{2020}
|
Example 3 Find all triples $(x, y, n), x, y, n \in \mathbf{N}^{\cdot}$ satisfying $\frac{x!+y!}{n!}=3^{n}$.
Translate the above text into English, please retain the original text's line breaks and format, and output the translation result directly.
|
(x,y,n)=(2,1,1),(1,2,1)
|
3. The minimum value of the function $y=|\cos x|+|\cos 2 x|(x \in \mathbf{R})$ is $\qquad$ .
|
\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}
|
【Question 22】
A reservoir has five water pipes. To fill the reservoir, the first four pipes together need 6 hours; the last four pipes together need 8 hours. If only the first and fifth pipes are opened, it takes 12 hours to fill the reservoir. How many hours will it take to fill the reservoir if only the fifth pipe is used?
|
48
|
4B. On the sides of a square with side length 2, isosceles trapezoids are constructed outward, such that the vertices of all trapezoids are simultaneously vertices of a regular dodecagon.
What is the perimeter of the dodecagon?
|
12(\sqrt{3}-1)
|
Example 4. Given $\sum_{j=1}^{n} a_{j} \cos \alpha_{j}=\sum_{j=1}^{n} a_{5} \cdot \cos \left(\alpha_{j}+1\right)=0$, find the value of $\sum_{j=1}^{n} a_{j} \cos \left(\alpha_{j}+\frac{\pi}{10}\right)$.
|
0
|
1. There are 2008 viewing stations set up along a circular marathon track, labeled as $c_{1}, c_{2}, \cdots, c_{2008}$ in a clockwise direction. These stations divide the track into 2008 segments. An athlete places mascots numbered $1, 2, \cdots, 2008$ at these stations in the following manner: He first places the 1st mascot at $c_{1}$, then runs clockwise over 29 segments and places the 2nd mascot at the station $c_{30}$; he then runs clockwise over 29 segments again and places the 3rd mascot at the station $c_{59}$, and so on. What is the number of the mascot placed at station $c_{2008}$?
(A) 2008 (B) 1896 (C) 1732 (D) 1731
|
1732
|
4. We will call a number greater than 25 semi-prime if it is the sum of some two distinct prime numbers. What is the maximum number of consecutive natural numbers that can be semi-prime?
|
5
|
7. (10 points) The teacher is doing calculation practice with Jiajia, Fangfang, and Mingming. The teacher first gives each of them a number, and then asks them to each pick 3 cards with numbers on them. Jiajia picks 3, 6, 7, Fangfang picks 4, 5, 6, and Mingming picks 4, 5, 8. The teacher then asks them to each multiply two of the numbers on their cards, and then add the number the teacher initially gave them. If the numbers the teacher initially gave them are 234, 235, 236 respectively, and they all calculate correctly, how many different numbers can they possibly get?
|
7
|
Given $\triangle{ABC}$ with $\angle{B}=60^{\circ}$ and $\angle{C}=30^{\circ}$, let $P,Q,R$ be points on the sides $BA,AC,CB$ respectively such that $BPQR$ is an isosceles trapezium with $PQ \parallel BR$ and $BP=QR$.\\
Find the maximum possible value of $\frac{2[ABC]}{[BPQR]}$ where $[S]$ denotes the area of any polygon $S$.
|
4
|
Three circles, with radii measuring 1, 2, and $3 \mathrm{~cm}$, are pairwise externally tangent, as shown in the given figure. Determine the radius of the circle that is externally tangent to the three circles.
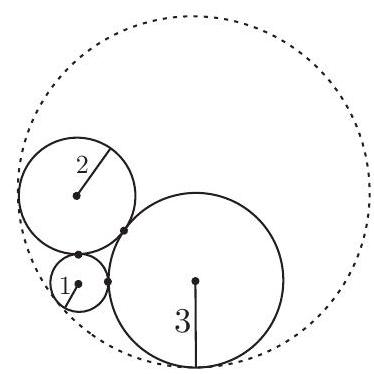
|
6
|
$11$ different books are on a $3$-shelf bookcase. In how many different ways can the books be arranged such that at most one shelf is empty?
$ \textbf{(A)}\ 75\cdot 11!
\qquad\textbf{(B)}\ 62\cdot 11!
\qquad\textbf{(C)}\ 68\cdot 12!
\qquad\textbf{(D)}\ 12\cdot 13!
\qquad\textbf{(E)}\ 6 \cdot 13!
$
|
75 \cdot 11!
|
8. As shown in Figure $11, \angle A O B=$ $30^{\circ}, \angle A O B$ contains a fixed point $P$, and $O P=10, O A$ has a point $Q, O B$ has a fixed point $R$. If the perimeter of $\triangle P Q R$ is minimized, find its minimum value.
|
10
|
11.1. Plot the graph of the function $\mathrm{y}=\sqrt{4 \sin ^{4} x-2 \cos 2 x+3}+\sqrt{4 \cos ^{4} x+2 \cos 2 x+3}$.
|
4
|
2. Let $A_{n}$ and $B_{n}$ be the sums of the first $n$ terms of the arithmetic sequences $\left\{a_{n}\right\}$ and $\left\{b_{n}\right\}$, respectively. If $\frac{A_{n}}{B_{n}}=\frac{5 n-3}{n+9}$, then $\frac{a_{8}}{b_{8}}=$ $\qquad$
|
3
|
17) On an island, there live three categories of people: the knights, who always tell the truth, the knaves, who always lie, and the pages, who after telling a truth always tell a lie and vice versa. On the island, I meet an old man, a boy, and a girl. The old man states: "I am a page"; "The boy is a knight."
The boy says: "I am a knight"; "The girl is a page."
The girl finally states: "I am a knave"; "The old man is a page."
It can then be said that among the three:
\(\begin{array}{ll}\text { (A) there is exactly one page } & \text { (B) there are exactly two pages }\end{array}\)
(C) there are exactly three pages (D) there is no page
(E) the number of pages is uncertain.
|
C
|
6. Three circles with radii $1,2,3$ touch each other externally. Find the radius of the circle passing through the three points of tangency of these circles.
|
1
|
Example 6 Given the sequence $\left\{a_{n}\right\}$ satisfies $a_{1}=a_{2}=1$, and $a_{n+2}=3 a_{n+1}+18 a_{n}+2^{n}\left(n \in \mathbf{N}_{+}\right)$.
Find $a_{n}$.
|
a_{n}=\frac{6^{n}}{12}-\frac{(-3)^{n}}{5}-\frac{2^{n}}{20}
|
XXXVIII OM - II - Task 1
From an urn containing one ball marked with the number 1, two balls marked with the number 2, ..., $ n $ balls marked with the number $ n $, we draw two balls without replacement. We assume that drawing each ball from the urn is equally probable. Calculate the probability that both drawn balls have the same number.
|
\frac{4}{3(n+2)}
|
12. A polyhedron, except for one vertex, the sum of the angles at the vertices of each face of the other vertices is $5160^{\circ}$, then the sum of the angles at the vertices of all faces of the polyhedron is $\qquad$
|
5400
|
G3.2 Let $a, b$ and $c$ be real numbers. If 1 is a root of $x^{2}+a x+2=0$ and $a$ and $b$ be roots of $x^{2}+5 x+c=0$, find the value of $a+b+c$.
|
1
|
$a$,$b$,$c$ are real. What is the highest value of $a+b+c$ if $a^2+4b^2+9c^2-2a-12b+6c+2=0$
|
\frac{17}{3}
|
22. In $\triangle A B C$, $D E, F G, M N, P Q, B C$ are mutually parallel, and $A D=D F=F M=M P=P B$, then $S_{\triangle A D E}: S_{D E G F}: S_{F G N M}: S_{M N Q P}: S_{P Q C B}=$ $\qquad$
|
1:3:5:7:9
|
2. Given $\alpha \in\left(0, \frac{\pi}{4}\right), t_{1}=(\tan \alpha)^{\tan \alpha}, t_{2}=$ $(\tan \alpha)^{\cot \alpha}, t_{3}=(\cot \alpha)^{\tan \alpha}, t_{4}=(\cot \alpha)^{\cot \alpha}$. Then the size relationship of $t_{1}, t_{2}, t_{3}, t_{4}$ is ( ).
(A) $t_{1}<t_{2}<t_{3}<t_{4}$
(B) $t_{2}<t_{1}<t_{3}<t_{4}$
(C) $t_{1}<t_{3}<t_{4}<t_{2}$
(D) cannot be determined
|
B
|
A1. When paying a deposit, we have to pay a $1.2\%$ fee. How many dollars will the fee amount to if we have to pay a deposit of 8000 SIT?
(A) 960
(B) 115
(C) 120
(D) 667
(E) 96
|
96
|
Equilateral triangle $ABC$ has side length $2$. A semicircle is drawn with diameter $BC$ such that it lies outside the triangle, and minor arc $BC$ is drawn so that it is part of a circle centered at $A$. The area of the “lune” that is inside the semicircle but outside sector $ABC$ can be expressed in the form $\sqrt{p}-\frac{q\pi}{r}$, where $p, q$, and $ r$ are positive integers such that $q$ and $r$ are relatively prime. Compute $p + q + r$.
[img]https://cdn.artofproblemsolving.com/attachments/7/7/f349a807583a83f93ba413bebf07e013265551.png[/img]
|
10
|
Three, (20 points) Find all functions $f: \mathbf{R} \rightarrow \mathbf{R}$ such that for any $x, y \in \mathbf{R}$, we have
$$
\begin{array}{l}
f(4 x-y-1)+4 f(x+y)-16 f(x) \\
=(6 x-2)^{2}+45 y^{2}
\end{array}
$$
|
f(x)=(3 x-1)^{2}
|
In a country there are $15$ cities, some pairs of which are connected by a single two-way airline of a company. There are $3$ companies and if any of them cancels all its flights, then it would still be possible to reach every city from every other city using the other two companies. At least how many two-way airlines are there?
|
21
|
3.12 Try to find the sum:
$$S=m!+\frac{(m+1)!}{1!}+\frac{(m+2)!}{2!}+\cdots+\frac{(m+n)!}{n!}$$
|
\frac{(m+n+1)!}{(m+1) \cdot n!}
|
36th BMO 2000 Problem 2 Find the smallest value of x 2 + 4xy + 4y 2 + 2z 2 for positive reals x, y, z with product 32. Solution
|
96
|
The target below is made up of concentric circles with diameters $4$, $8$, $12$, $16$, and $20$. The area of the dark region is $n\pi$. Find $n$.
[asy]
size(150);
defaultpen(linewidth(0.8));
int i;
for(i=5;i>=1;i=i-1)
{
if (floor(i/2)==i/2)
{
filldraw(circle(origin,4*i),white);
}
else
{
filldraw(circle(origin,4*i),red);
}
}
[/asy]
|
60
|
4. Find all real solutions to $x^{3}+(x+1)^{3}+(x+2)^{3}=(x+3)^{3}$.
|
3
|
8. Given the set
$$
\begin{array}{c}
A_{k}=\left\{2^{k-1}+\sum_{i=0}^{k-2} a_{i} 2^{a_{i}+i} \mid a_{i} \in\{0,1\},\right. \\
i=0,1, \cdots, k-2\} .
\end{array}
$$
Let $n_{k}$ denote the sum of all elements in the set $A_{k}$. Then $\sum_{k=1}^{2015} n_{k}=$ $\qquad$
|
\frac{2^{4031}+1}{3}-2^{2015}
|
2. Each of the three boys either always tells the truth or always lies. They were told six natural numbers. After that, each boy made two statements.
Petya: 1) These are six consecutive natural numbers.
2) The sum of these six numbers is even.
Vasya: 1) These are the numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6.
2) Kolya is a liar.
Kolya: 1) All these numbers are different and divisible by 3.
2) Each of these numbers is less than 20.
What numbers were told to the boys?
|
3,6,9,12,15,18
|
Example 12 Let $a_{1}, a_{2}, \cdots, a_{n}, \cdots$ be a non-decreasing sequence of positive integers. For $m \geqslant 1$, define $b_{m}=\min \left\{n, a_{n} \geqslant m\right\}$, i.e., $b_{m}$ is the smallest value of $n$ such that $a_{n} \geqslant m$. Given that $a_{19}=85$, find
$$a_{1}+a_{2}+\cdots+a_{19}+b_{1}+b_{2}+\cdots+b_{85}$$
the maximum value.
|
1700
|
1. Let $a_{1}, a_{2}, \ldots, a_{n}$ be integers $(n>1)$ satisfying $a_{1}+a_{2}+\cdots+a_{n}=a_{1} a_{2} \cdots a_{n}=2005$. Find the smallest possible value of $n$.
(1 mark)
Let $a_{1}, a_{2}, \ldots, a_{n}$ be integers $(n>1)$, such that $a_{1}+a_{2}+\cdots+a_{n}=a_{1} a_{2} \cdots a_{n}=2005$. Find the smallest possible value of $n$.
|
5
|
14. In a sequence, each term after the first two terms is the mean of all the terms which come before that term. The first term is 8 and the tenth term is 26 . What is the second term?
A 17
B 18
C 44
D 52
E 68
|
44
|
6.030. $\left(\frac{x^{2}+6}{x^{2}-4}\right)^{2}=\left(\frac{5 x}{4-x^{2}}\right)^{2}$.
|
x_{1}=-3,x_{2}=3
|
1. Given vectors $\boldsymbol{a}$ and $\boldsymbol{b}$ satisfy:
$$
\begin{array}{l}
|a-b|=3,|a+2 b|=6, \\
a^{2}+a \cdot b-2 b^{2}=-9 .
\end{array}
$$
Then $|b|=$ $\qquad$
|
\sqrt{7}
|
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.