problem
stringlengths 18
2.25k
| gt
stringlengths 1
173
|
|---|---|
Solve in positive integers the following equation $$\left [\sqrt{1}\right]+\left [\sqrt{2}\right]+\left [\sqrt{3}\right]+\ldots+\left [\sqrt{x^2-2}\right]+\left [\sqrt{x^2-1}\right]=125,$$ where $[a]$ is the integer part of the real number $a$.
|
6
|
15 Find the maximum value of the positive real number $A$ such that for any real numbers $x, y, z$, the inequality
$$
x^{4}+y^{4}+z^{4}+x^{2} y z+x y^{2} z+x y z^{2}-A(x y+y z+z x)^{2} \geqslant 0
$$
holds.
|
\frac{2}{3}
|
2. Given $a<0$, then $\sqrt{(2 a-|a|)^{2}}$ equals ( ).
(A) $a$
(B) $-a$
(C) $3 a$
(D) $-3 a$
|
D
|
Point $A,B$ are marked on the right branch of the hyperbola $y=\frac{1}{x},x>0$. The straight line $l$ passing through the origin $O$ is perpendicular to $AB$ and meets $AB$ and given branch of the hyperbola at points $D$ and $C$ respectively. The circle through $A,B,C$ meets $l$ at $F$.
Find $OD:CF$
|
1:2
|
Tetrahedron $ABCD$ has $AD=BC=28$, $AC=BD=44$, and $AB=CD=52$. For any point $X$ in space, suppose $f(X)=AX+BX+CX+DX$. The least possible value of $f(X)$ can be expressed as $m\sqrt{n}$, where $m$ and $n$ are positive integers, and $n$ is not divisible by the square of any prime. Find $m+n$.
|
682
|
3. Let $O$ be the origin, $A$ be a moving point on the parabola $x=\frac{1}{4} y^{2}+1$, and $B$ be a moving point on the parabola $y=x^{2}+4$. Then the minimum value of the area of $\triangle O A B$ is $\qquad$ .
|
2
|
14. Asymmetric coin. (From 9th grade, 2 points) Billy Bones has two coins - a gold one and a silver one. One of them is symmetric, and the other is not. It is unknown which coin is asymmetric, but it is known that the asymmetric coin lands heads with a probability of \( p = 0.6 \).
Billy Bones tossed the gold coin, and heads came up immediately. Then Billy Bones started tossing the silver coin, and heads came up only on the second toss. Find the probability that the asymmetric coin is the gold one.
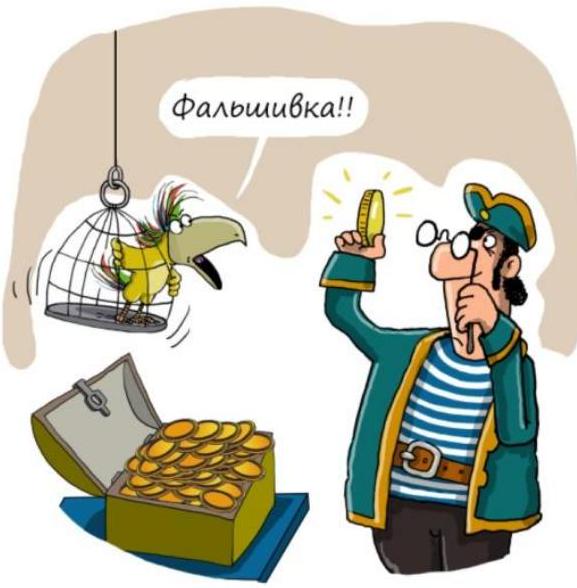

|
\frac{5}{9}
|
5. Several people played a round-robin table tennis tournament. At the end of the tournament, it turned out that for any four participants, there would be two who scored the same number of points in the games between these four participants. What is the maximum number of tennis players that could have participated in this tournament? In table tennis, there are no ties; one point is awarded for a win, and zero points for a loss.
(from materials of international olympiads)
|
7
|
## Task 2.
A frog is located at the origin $O$ of a number line and needs to perform 2022 jumps, each of a different length from $1, 2, \ldots, 2022$. The jumps must be performed in such an order that the following rules are respected:
- if the frog is currently at point $O$ or to the left of it, it must jump to the right,
- if the frog is to the right of point $O$, it must jump to the left.
Determine the largest natural number $k$ for which the frog can jump in such a way that it never lands on any of the numbers $1, 2, \ldots, k$.
|
1010
|
8. Arrange the $n$ consecutive positive integers from 1 to $n$ ($n>1$) in a sequence such that the sum of every two adjacent terms is a perfect square. The minimum value of $n$ is $\qquad$ .
|
15
|
8. Arrange the $n$ consecutive positive integers from 1 to $n$ ($n>1$) in a sequence such that the sum of every two adjacent terms is a perfect square. The minimum value of the positive integer $n$ is $\qquad$ .
|
15
|
1. Given quadratic trinomials $f_{1}(x)=x^{2}+2 x+a, f_{2}(x)=x^{2}+b x-1, f_{3}(x)=2 x^{2}+(6-b) x+3 a+1$ and $f_{4}(x)=2 x^{2}+(3 b-2) x-a-3$. Let the differences of their roots be $A, B, C$ and $D$, respectively, and given that $|A| \neq|B|$. Find the ratio $\frac{C^{2}-D^{2}}{A^{2}-B^{2}}$. The values of $A, B, C, D, a, b$ are not specified.
|
2
|
Example 24([43.3]) Find all pairs of positive integers $\{m, n\}(m \geqslant 3, n \geqslant 3)$ such that there exist infinitely many positive integers $a$ for which the value of $\frac{a^{m}+a-1}{a^{n}+a^{2}-1}$ is an integer.
|
m=5, n=3
|
2. Two Ultramen are fighting a monster, which can withstand 100 attacks. One Ultraman can attack 12 times per minute, and the other can attack 8 times per minute. If the two Ultramen start attacking together, they can defeat the monster in $\qquad$ minutes.
|
5
|
【Question 11】
Xiao Ling is reading an interesting storybook. Every day she reads twice the number of pages she has read in the previous days, and on the sixth day, she read $\frac{1}{9}$ of the book. On which day did Xiao Ling finish reading the book?
|
8
|
## Task 5/73
Determine all prime numbers of the form $p=x^{4}+4 y^{4}$, where x and y are natural numbers.
|
5
|
Task A-2.6. (10 points)
Determine all natural numbers less than 1000 that are equal to the sum of the squares of their digits.
|
1
|
6. The graph of the linear function $y=k(x-1)$ passes through the point $M(-1,-2)$. Then its intersection with the $y$-axis is ( ).
(A) $(0,-1)$
(B) $(1,0)$
(C) $(0,0)$
(D) $(0,1)$
|
A
|
4.013. The sum of the first three terms of an increasing arithmetic progression is 15. If 1 is subtracted from the first two terms of this progression, and 1 is added to the third term, the resulting three numbers will form a geometric progression. Find the sum of the first 10 terms of the arithmetic progression.
|
120
|
11. Given real numbers $x_{1}, x_{2}, x_{3}$ satisfy: $x_{1}^{2}+x_{2}^{2}+x_{3}^{2}+x_{1} x_{2}+x_{2} x_{3}=2$, then the maximum value of $\left|x_{2}\right|$ is $\qquad$
|
2
|
9. $\tan 20^{\circ} \csc 60^{\circ}\left(\csc 10^{\circ}-1\right)=$
|
2
|
G3.3 Given that $\tan x+\tan y+1=\cot x+\cot y=6$. If $z=\tan (x+y)$, find the value of $z$.
|
30
|
Example 2 Use $[a]$ to denote the greatest integer not exceeding the real number $a$, and $\{a\}=a-[a]$ to denote the fractional part of $a$. Solve the equation $\left[x^{3}\right]+\left[x^{2}\right]+[x]=\{x\}-1$.
(1991, Shanghai Junior High School Mathematics Competition)
|
x=-1
|
258. It is known that
$$
\begin{array}{r}
a_{1}-4 a_{2}+3 a_{3} \geqslant 0 \\
a_{2}-4 a_{3}+3 a_{4} \geqslant 0 \\
\cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot \\
\cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot \\
a_{98}-4 a_{99}+3 a_{100} \geqslant 0 \\
a_{99}-4 a_{100}+3 a_{1} \geqslant 0 \\
a_{100}-4 a_{1}+3 a_{2} \geqslant 0
\end{array}
$$
Let $a_{1}=1$; what are the numbers $a_{2}, a_{3}, \ldots, a_{100}$ then?
|
a_{2}=a_{3}=\ldots=a_{100}=1
|
$$
\begin{array}{ll}
10-6-4 & 12+8-3 \\
11+5+0 & 18-6+6
\end{array}
$$
Task 1
$$
\begin{array}{ll}
10-6-4 & 12+8-3 \\
11+5+0 & 18-6+6
\end{array}
$$
|
0,17,16,18
|
2. Let $a=\sqrt{3}-\sqrt{2}, b=2-\sqrt{3}, c=$ $\sqrt{\sqrt{5}-2}$. Then the size relationship of $a, b, c$ is ( ).
(A) $c>a>b$
(B) $ab>c$
(D) $a>c>b$
|
A
|
## Task B-3.4.
What is the area of a triangle whose sum of the squares of the side lengths is 2016, and the sum of the cotangents of the angles is 18?
|
28
|
2.1. Solve the equation $\sqrt{x+\sqrt{4 x+\sqrt{16 x+3}}}-\sqrt{x}=1$.
|
\frac{1}{16}
|
7、The denominator is a two-digit number, the numerator is 1, and the fraction can be converted into a finite decimal. There are $\qquad$
The fraction has a two-digit denominator, a numerator of 1, and can be converted into a finite decimal. There are $\qquad$
|
9
|
15. Let $\left\{a_{n}\right\}$ be a geometric sequence, and each term is greater than
1. Then
$$
\lg a_{1} \cdot \lg a_{2012} \sum_{i=1}^{2011} \frac{1}{\lg a_{i} \cdot \lg a_{i+1}}=
$$
$\qquad$
|
2011
|
In an isosceles triangle, the base is one unit, and the length of the legs is $b$. What is the base of an isosceles triangle whose vertex angle is equal to the base angle of the previous triangle and whose legs are one unit long?
|
\sqrt{2-\frac{1}{b}}
|
1. The page numbers of a book range from 1 to $n$. When all these page numbers are added together, one of the page numbers was mistakenly added twice. The incorrect sum obtained is 1987. What is the page number that was added twice?
|
34
|
Determine the smallest integer $n$ such that there exist $n$ real numbers $x_{1}, \ldots, x_{n}$ all belonging to the interval $(-1,1)$ and for which
$$
x_{1}+\cdots+x_{n}=0 \quad \text { and } \quad x_{1}^{2}+\cdots+x_{n}^{2}=2020
$$
|
2022
|
1. For every natural number $n$ with 3 decimal digits (so the first digit is not zero), we consider the number $n_{0}$ obtained from $n$ by removing its digits that are equal to zero. For example, if $n=205$ then $n_{0}=25$.
Determine the number of integers $n$ with three digits for which $n_{0}$ is a divisor of $n$ different from $n$.
|
93
|
6. (10 points) There is a special calculator. When a number is input, the calculator multiplies this number by 2, then reverses the order of the digits of the result, and finally adds 2 to display the final result. If a two-digit number is input, and the final result displayed is 45, then the number initially input was $\qquad$
|
17
|
A tree has $10$ pounds of apples at dawn. Every afternoon, a bird comes and eats $x$ pounds of apples. Overnight, the amount of food on the tree increases by $10\%$. What is the maximum value of $x$ such that the bird can sustain itself indefinitely on the tree without the tree running out of food?
|
\frac{10}{11}
|
12. The parabolas $y=x^{2}-b x$, $y=-x^{2}+b x$ and the line $y=k x$ can divide the plane into at most
$\qquad$ parts.
|
9
|
1. What is the maximum number of sides a convex polygon can have if all its diagonals are of equal length?
|
5
|
* Four, the sequence $1,1,3,3,3^{2}, 3^{2}, \cdots, 3^{1992}, 3^{1992}$ consists of two 1s, two 3s, two $3^{2}$s, ..., two $3^{1992}$s arranged in ascending order. The sum of the terms in the sequence is denoted as $S$. For a given natural number $n$, if it is possible to select some terms from different positions in the sequence such that their sum is exactly $n$, it is called a selection scheme, and the number of all selection schemes with the sum $n$ is denoted as $f(n)$. Try to find:
$$
f(1)+f(2)+\cdots+f(s) \text { . }
$$
|
4^{1993}-1
|
Example 3: In front of each number in $1, 2, 3, \cdots, 1989$, add a “+” or “-” sign to make their algebraic sum the smallest non-negative number, and write out the equation.
(1989, All-Russian Mathematical Olympiad)
|
1
|
Problem 4. On the segment $A B$, a point $C$ is chosen. The segment $A B$ is 4 times longer than the segment $A C$. Determine the lengths of the segments $A B$ and $A C$, if the length of the segment $C B$ is $24 \mathrm{~cm}$.
|
AC=8\mathrm{~},AB=32\mathrm{~}
|
Example 2 Choose five different numbers from $1,2, \cdots, 20$, the probability that at least two of them are consecutive numbers is $\qquad$ . [1]
|
\frac{232}{323}
|
18. Find all integers $n$ for which $n^{5}+3$ is divisible by $n^{2}+1$.
|
-3,-1,0,1,2
|
$32 \cdot 26$ Let $n$ be a natural number between 100 and 200, then the number of $n$ that satisfies $7 n+2$ is a multiple of 5 is
(A) 10.
(B) 11.
(C) 20.
(D) 21.
(2nd "Five Sheep Cup" Junior High School Mathematics Competition, 1990)
|
20
|
Twelve congruent disks are placed on a circle $C$ of radius 1 in such a way that the twelve disks cover $C$, no two of the disks overlap, and so that each of the twelve disks is tangent to its two neighbors. The resulting arrangement of disks is shown in the figure below. The sum of the areas of the twelve disks can be written in the from $\pi(a-b\sqrt{c})$, where $a,b,c$ are positive integers and $c$ is not divisible by the square of any prime. Find $a+b+c$.
[asy]
real r=2-sqrt(3);
draw(Circle(origin, 1));
int i;
for(i=0; i<12; i=i+1) {
draw(Circle(dir(30*i), r));
dot(dir(30*i));
}
draw(origin--(1,0)--dir(30)--cycle);
label("1", (0.5,0), S);[/asy]
|
135
|
7. Let $f(x)$ satisfy the equation $f(x)-2 f\left(\frac{1}{x}\right)=x$. Then the range of $f(x)$ is $\qquad$ .
|
\left(-\infty,-\frac{2 \sqrt{2}}{3}\right] \cup\left[\frac{2 \sqrt{2}}{3},+\infty\right)
|
2. The sequence $\left(a_{n}\right)$ is defined by the following relations: $a_{1}=1, a_{2}=2, a_{n}=a_{n-1}-a_{n-2}+n$ (for $n \geqslant 3$). Find $a_{2019}$.
|
2020
|
## Problem Statement
Calculate the definite integral:
$$
\int_{0}^{6} \frac{e^{\sqrt{(6-x) /(6+x)}} \cdot d x}{(6+x) \sqrt{36-x^{2}}}
$$
|
\frac{e-1}{6}
|
7.1. Come up with at least one three-digit PAU number (all digits are different) such that $(П+\mathrm{A}+\mathrm{У}) \times \Pi \times \mathrm{A} \times \mathrm{Y}=300$ (it is sufficient to provide one example)
|
235
|
Example 7.17 Use red, blue, and yellow to paint the 6 faces of a cube, so that 2 faces are painted red, 2 faces are painted blue, and 2 faces are painted yellow. Find the number of distinct colored cubes that can be formed.
|
6
|
4. Given real numbers $x, y$ satisfy $\frac{x^{2}}{3}+y^{2}=1$. Then
$$
P=|2 x+y-4|+|4-x-2 y|
$$
the range of values for $P$ is . $\qquad$
|
[2,14]
|
8.2. Two cyclists, Andrey and Boris, are riding at a constant and identical speed along a straight highway in the same direction, so that the distance between them remains constant. There is a turnoff to a village ahead. At some point in time, the distance from Andrey to the turnoff was equal to the square of the distance from Boris to the same turnoff. When each of them had traveled another 1 km, the distance from Andrey to the turnoff became three times the distance from Boris to the turnoff. What is the distance between the cyclists?
|
2
|
【Question 4】
The sum of the digits of a three-digit number is 18, the hundreds digit is 1 more than the tens digit, and the units digit is 2 more than the tens digit. This three-digit number is $\qquad$.
|
657
|
11. Given the sequence $\left\{a_{n}\right\}$, the sum of the first $n$ terms is
$$
S_{n}=2 a_{n}-2\left(n \in \mathbf{Z}_{+}\right) \text {. }
$$
(1) Find the general term formula $a_{n}$;
(2) Let $b_{n}=\frac{1}{a_{n}}-\frac{1}{n(n+1)}, T_{n}$ be the sum of the first $n$ terms of the sequence $\left\{b_{n}\right\}$, find the positive integer $k$ such that for any $n \in$ $\mathbf{Z}_{+}$, we have $T_{k} \geqslant T_{n}$;
(3) Let $c_{n}=\frac{a_{n+1}}{\left(1+a_{n}\right)\left(1+a_{n+1}\right)}, R_{n}$ be the sum of the first $n$ terms of the sequence $\left\{c_{n}\right\}$, if for any $n \in \mathbf{Z}_{+}$, we have $R_{n}<\lambda$, find the minimum value of $\lambda$.
|
\frac{2}{3}
|
Example 4 As shown in Figure 4, in $\triangle A B C$, $A B=A C, \angle A$ $=100^{\circ}, I$ is the incenter, and $D$ is a point on side $A B$ such that $B D=B I$. Find the measure of $\angle B C D$.
Translate the above text into English, please keep the original text's line breaks and format, and output the translation result directly.
|
30
|
12 The number of arithmetic sequences that satisfy the first term is 1783, the last term is 1993, the number of terms is no less than 3, and the common difference is a natural number greater than 2 is
A. 12
B. 13
C. 14
D. 15
|
13
|
Exercise 11. A palette of 6 different colors is given. In how many ways can a cube be painted, using all 6 colors, and exactly one color per face? Two ways of coloring are considered identical if one can be obtained from the other by any rotation in space.
|
30
|
1. Given the sequence $\left\{a_{n}\right\}$ with the general term formula $a_{n}=\log _{3}\left(1+\frac{2}{n^{2}+3 n}\right)$, then $\lim _{n \rightarrow \infty}\left(a_{1}+a_{2}+\cdots+a_{n}\right)=$
|
1
|
In the diagram, point $Q$ is the midpoint of $P R$. The coordinates of $R$ are
(A) $(2,5)$
(B) $(7,11)$
(C) $(6,9)$
(D) $(8,10)$
(E) $(9,15)$
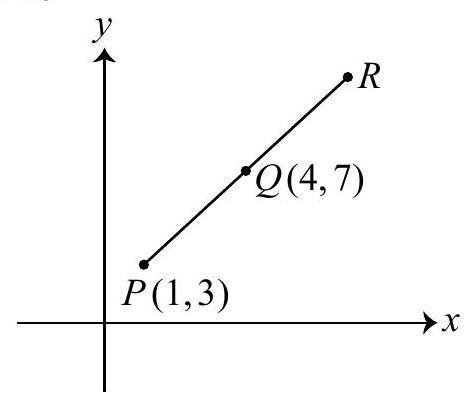
|
(7,11)
|
1. Find the last three digits of $9^{100}-1$.
|
0
|
At the "Lukomorye" station, they sell cards for one, five, and twenty rides. All cards cost a whole number of gold coins. Five cards for one ride are more expensive than one card for five rides, and four cards for five rides are more expensive than one card for twenty rides. It turned out that the cheapest way for 33 bogatyrs to travel is to buy cards for 35 rides, spending 33 gold coins on this. How much does a card for five rides cost?
|
5
|
3. A set of 55 dominoes contains all possible combinations of two numbers from 0 to 9, including dominoes with the same number on both ends. (In the image, three dominoes are shown: a domino with the numbers 3 and 4, a domino with the numbers 0 and 9, and a domino with the number 3 on both ends.) How many dots are there in total in the entire set of dominoes?

|
495
|
Task B-2.3. Andrea and Mirela are preparing for a math competition. When their teacher asked them how many problems they solved yesterday, they did not answer directly. He only found out that Andrea solved fewer problems than Mirela, and each of them solved at least one problem. They also said that the product of the number of problems solved by Andrea and the number of problems solved by Mirela, increased by their sum, is equal to 59. How many problems did Andrea solve? How many different answers are there to this question?
|
5
|
Example 6 Given a complex number $z$ satisfying $|z|=1$, try to find the maximum value of $u=\left|z^{3}-3 z+2\right|$.
(2000 Jilin Province High School Competition)
|
3\sqrt{3}
|
$36 \cdot 66$ There are three piles of stones with numbers $2,3,4$. Two people take turns to take away stones, the rule is: each person must take at least 1 stone each time, no limit on how many more, but must take from the same pile, the one who takes the last 1 stone loses. Then the winning strategy is
(A) The first player has.
(B) The second player has.
(C) Both have.
(D) Neither has.
(3rd "Five Sheep Cup" Junior High School Mathematics Competition, 1991)
|
A
|
The sum
$$\frac{1^2-2}{1!} + \frac{2^2-2}{2!} + \frac{3^2-2}{3!} + \cdots + \frac{2021^2 - 2}{2021!}$$
$ $ \\
can be expressed as a rational number $N$. Find the last 3 digits of $2021! \cdot N$.
|
977
|
1. Does the number 1... (1000 ones) have a ten-digit divisor, all digits of which are different?
|
No
|
Example 2 Divide a circle into $n(n \geqslant 2)$ sectors, each sector is colored with one of $r$ different colors, and it is required that adjacent sectors are colored differently. Question: How many coloring methods are there?
|
a_{n}=(r-1)(-1)^{n}+(r-1)^{n}
|
Given a positive integer $N$ (written in base 10), define its integer substrings to be integers that are equal to strings of one or more consecutive digits from $N$, including $N$ itself. For example, the integer substrings of 3208 are $3,2,0,8,32,20,320,208$, and 3208. (The substring 08 is omitted from this list because it is the same integer as the substring 8 , which is already listed.)
What is the greatest integer $N$ such that no integer substring of $N$ is a multiple of 9? (Note: 0 is a multiple of 9.)
|
88,888,888
|
## Task 3 - V00803
I drop a ball. It bounces up to $\frac{2}{3}$ of its falling height. It falls again and bounces the second time $\frac{5}{8}$ of the first bounce height.
Calculate from what height I dropped the ball if it bounced $45 \mathrm{~cm}$ less high the second time than the first time!
|
180
|
(a) Three lines $l,m,n$ in space pass through point $S$. A plane perpendicular to $m$ intersects $l,m,n $ at $A,B,C$ respectively. Suppose that $\angle ASB = \angle BSC = 45^o$ and $\angle ABC = 90^o$. Compute $\angle ASC$.
(b) Furthermore, if a plane perpendicular to $l$ intersects $l,m,n$ at $P,Q,R$ respectively and $SP = 1$, find the sides of triangle $PQR$.
|
PQ = 1, QR = \sqrt{2}, PR = \sqrt{3}
|
30.4. In an arithmetic sequence, the third, fifth and eleventh terms are distinct and form a geometric sequence. If the fourth term of the arithmetic sequence is 6 , what is its 2007 th term?
|
6015
|
1.2. Compute the double integral
$$
\iint_{\Omega}(x+y) d x d y
$$
where $\Omega$ is the triangle formed by the lines:
a) $x=0 ; y=0 ; x+y=3$;
b) $x=3 ; y=0 ; y=x$.

|
\frac{27}{2}
|
02.2. In two bowls there are in total $N$ balls, numbered from 1 to $N$. One ball is moved from one of the bowls to the other. The average of the numbers in the bowls is increased in both of the bowls by the same amount, $x$. Determine the largest possible value of $x$.
|
\frac{1}{2}
|
Exercise 5. In a classroom, there are ten students. Aline writes ten consecutive integers on the board. Each student chooses one of the ten integers written on the board, such that any two students always choose two different integers. Each student then calculates the sum of the nine integers chosen by the other nine students. Each student whose result is a perfect square then receives a gift.
What is the maximum number of students who will receive a gift?
A perfect square is an integer of the form $n^{2}$, where $n$ is a natural number.
|
4
|
12. The condition for the function $f(x)=3 \sin (2 x+\theta)$ to be an even function is (
(A) $\theta=k \pi+\frac{\pi}{2}(k \in Z)$
(B) $\theta=k \pi+\pi(k \in Z)$
(C) $\theta=2 k \pi+\frac{\pi}{2}(k \in Z)$
(D) $\theta=2 k \pi+\pi(k \in Z)$
|
A
|
5. Circles $K_{1}$ and $K_{2}$ with centers at points $O_{1}$ and $O_{2}$ have the same radius $r$ and touch the circle $K$ of radius $R$ with center at point $O$ internally. The angle $O_{1} O O_{2}$ is $120^{\circ}$. Find the radius $q$ of the circle that touches $K_{1}$ and $K_{2}$ externally and the circle $K$ internally.
|
\frac{R(R-r)}{R+3r}
|
Find the positive constant $c_0$ such that the series \[ \displaystyle\sum_{n = 0}^{\infty} \dfrac {n!}{(cn)^n} \] converges for $c>c_0$ and diverges for $0<c<c_0$.
|
\frac{1}{e}
|
Let's determine the ratio $x: y: z$ if
$$
(5 x+4 y-6 z):(4 x-5 y+7 z):(6 x+5 y-4 z)=1: 27: 18
$$
|
3:4:5
|
## Task A-2.1.
Let $a, b, c$ and $d$ be distinct real numbers. If $a$ and $b$ are solutions to the equation $x^{2}-10 c x-11 d=0$, and $c$ and $d$ are solutions to the equation $x^{2}-10 a x-11 b=0$, determine the sum $a+b+c+d$.
|
1210
|
Caden, Zoe, Noah, and Sophia shared a pizza. Caden ate 20 percent of the pizza. Zoe ate 50 percent more of the pizza than Caden ate. Noah ate 50 percent more of the pizza than Zoe ate, and Sophia ate the rest of the pizza. Find the percentage of the pizza that Sophia ate.
|
5\%
|
A dog took a hare to the hunt, which has a 50-jump lead. The dog makes 5 jumps while the hare makes 6, but 7 of the dog's jumps equal 9 of the hare's jumps. How many more jumps can the hare make before the dog catches up?
|
700
|
7.016. If $\log _{a} 27=b$, then what is $\log _{\sqrt{3}} \sqrt[6]{a}$?
|
\frac{1}{b}
|
10. (1983 AIME, Problem 1) What is the greatest two-digit prime factor of the integer $C_{200}^{100}$?
|
61
|
5. In $\triangle A B C$, it is known that $A B=A C$, point $D$ is on side $A C$, $\angle A D B=60^{\circ}$, point $E$ is on side $B D$, $\angle E C B=30^{\circ}$. Find the degree measure of $\angle A E C$.
|
150^{\circ}
|
1. There are two positive integers, one of which is a square number. If the sum of the two numbers is 2006 smaller than their product, find the difference between the two numbers.
(1 mark)現有兩個正整數, 其中一個是平方數。若兩數之和比它們之積小 2006 , 求兩數之差。
|
666
|
8. Let the sequence $a_{n}=\left[(\sqrt{2}+1)^{n}+\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^{n}\right], n \geq 0$, where $[x]$ denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to $x$. Then
$$
\sum_{n=1}^{\infty} \frac{1}{a_{n-1} a_{n+1}}=
$$
|
\frac{1}{8}
|
3. Among the four functions $y=\sin |x|, y=\cos |x|, y=|\cot x|, y=\lg |\sin x|$, the even function that is periodic with $\pi$ and monotonically increasing in $\left(0, \frac{\pi}{2}\right)$ is
(A) $y=\sin |x|$
(B) $y=\cos |x|$
(C) $y=|\cot x|$
(D) $y=\lg |\sin x|$
|
D
|
6. $A$ is the foot of the mountain, $B$ is the peak, and $C$ is a point on the slope, with $A C=\frac{1}{3} A B$. Person A and Person B start from the foot of the mountain at the same time, reach the peak, and return to the foot, repeating this back-and-forth movement. The speed ratio of A to B is $6: 5$, and the downhill speed of both A and B is 1.5 times their respective uphill speeds. After some time, A first sees B climbing on the $A C$ segment from the peak; after some more time, A sees B climbing on the $A C$ segment from the peak for the second time. How many times has A reached the peak by the time A sees B climbing on the $A C$ segment for the second time (including this time)?
|
9
|
Problem 6. A convex quadrilateral $ABCD$ is such that $\angle BAC = \angle BDA$ and $\angle BAD = \angle ADC = 60^{\circ}$. Find the length of $AD$, given that $AB = 14$ and $CD = 6$.
Answer: 20.
|
20
|
$\mathrm{Az}$
$$
a_{n}=\frac{(n+3)^{2}+3}{n(n+1)(n+2)} \cdot \frac{1}{2^{n+1}}
$$
is a sequence defined by its general term. We form the sequence
$$
b_{n}=\sum_{k=1}^{n} a_{k}
$$
Determine the limit of the sequence $b_{n}$ as $n \rightarrow+\infty$.
|
1
|
12. find all natural numbers that are in the form
$$
\frac{(a+b+c)^{2}}{a b c}
$$
where $a, b$ and $c$ are natural numbers.
|
1,2,3,4,5,6,8,9
|
In triangle $ABC$, let $I, O, H$ be the incenter, circumcenter and orthocenter, respectively. Suppose that $AI = 11$ and $AO = AH = 13$. Find $OH$.
[i]Proposed by Kevin You[/i]
|
10
|
14th Mexico 2000 Problem B1 Given positive integers a, b (neither a multiple of 5) we construct a sequence as follows: a 1 = 5, a n+1 = a a n + b. What is the largest number of primes that can be obtained before the first composite member of the sequence?
|
5
|
1. The maximum value of the function $y=\sin ^{4} x \cdot \cos x+\sin x \cdot \cos ^{4} x$ $\left(0<x<\frac{\pi}{2}\right)$ is $\qquad$ .
|
\frac{\sqrt{2}}{4}
|
27. There are 4 letters $A, B, C, D$ and 3 mailboxes numbered 1, 2, 3. If the 4 letters can be placed in any of the mailboxes, until all are placed. Find: (1) the probability that mailbox 3 has exactly 1 letter; (2) the probability that letter A is placed in mailbox 1 or 2.
|
\frac{32}{81},\frac{2}{3}
|
1. Given the function
$$
f(x)=\frac{1+2 x-x^{2}}{(1+x)\left(1+x^{2}\right)} \text {. }
$$
Let $\alpha, \beta, \gamma$ be the three interior angles of an arbitrary acute triangle. Then
$$
\begin{array}{l}
f(\tan \alpha)+f(\tan \beta)+f(\tan \gamma)+ \\
f(\cot \alpha)+f(\cot \beta)+f(\cot \gamma)=
\end{array}
$$
|
3
|
5. Given two points $A(0,1), B(6,9)$. If there is an integer point $C$ (Note: A point with both coordinates as integers is called an integer point), such that the area of $\triangle A B C$ is minimized. Then the minimum value of the area of $\triangle A B C$ is $\qquad$
|
1
|
7.205. $|x-3|^{3 x^{2}-10 x+3}=1$.
7.205. $|x-3|^{3 x^{2}-10 x+3}=1$.
|
\frac{1}{3};2;4
|
6. Randomly select 3 vertices from a regular 11-sided polygon, the probability that they form an acute triangle is
保留源文本的换行和格式,直接输出翻译结果如下:
6. Randomly select 3 vertices from a regular 11-sided polygon, the probability that they form an acute triangle is
|
\frac{1}{3}
|
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.